Enhancing the Performance of 2D Tin-Based Pure Red Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes through the Synergistic Effect of Natural Antioxidants and Cyclic Molecular Additives
C.-H. Chen, M.-H. Yu, Y.-Y. Wang, Y.-C. Tseng, I. Chao, I. Ni, B.-H. Lin, Y.-J. Lu, C.-C. Chueh, Small 2024, 20, 2307774. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202307774
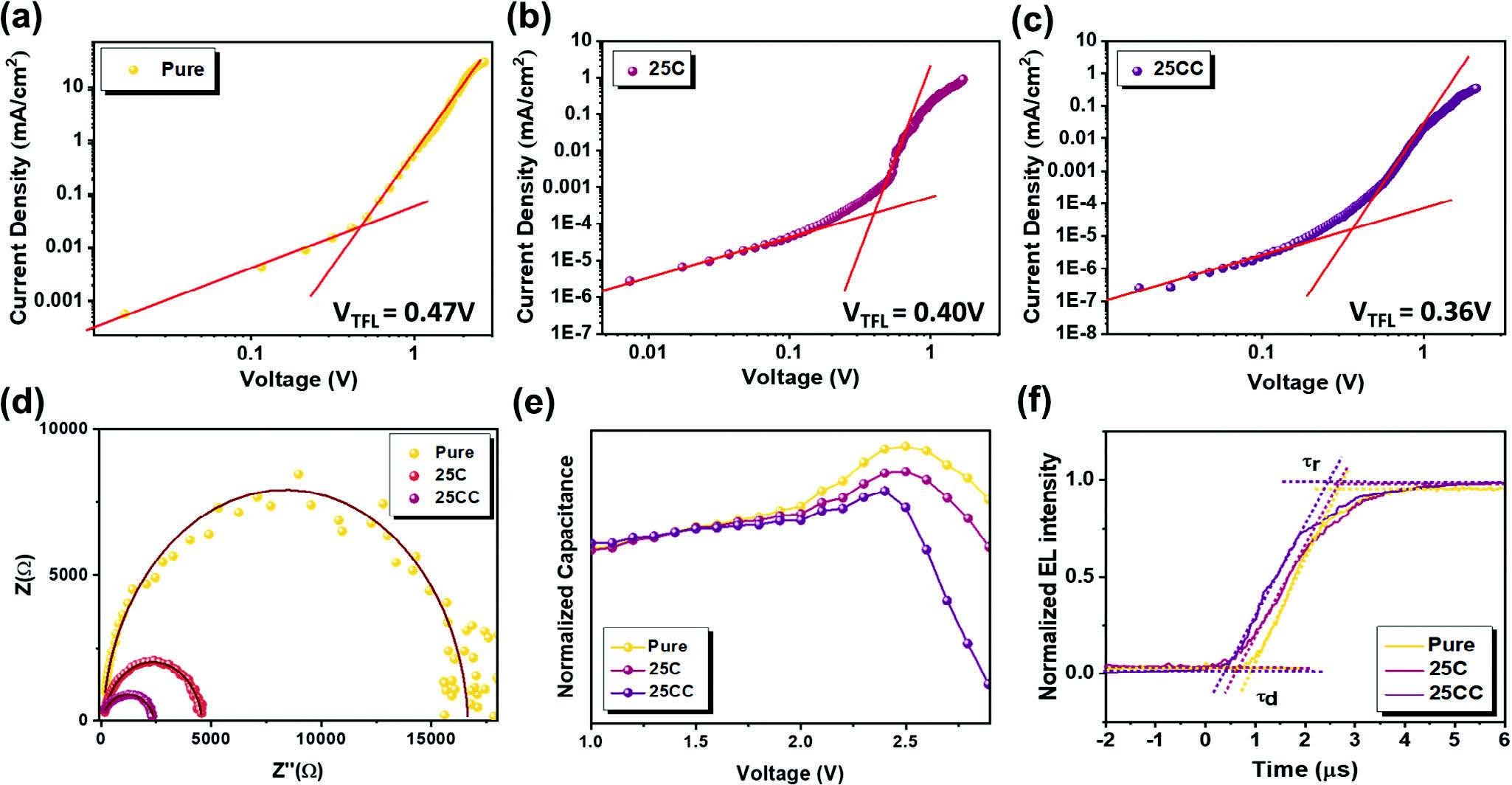
The research investigates the enhancement of 2D tin-based pure red perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) using a dual-additive approach involving natural antioxidants and cyclic molecular additives. Specifically, ascorbic acid (VitC) is used to prevent the oxidation of Sn²⁺ to Sn⁴⁺ and improve film quality, while 18-Crown-6 is added to capture excess ions and synergistically reduce nonradiative recombination pathways. This combination significantly improves the PeLEDs' performance, achieving a maximum external quantum efficiency of 1.87%, which is approximately nine times higher than the pristine device. The study highlights the potential of environmentally friendly additives to enhance the stability and efficiency of Sn-based perovskite films for sustainable optoelectronic applications.
Use and Value of Paios
Paios, the all-in-one characterization tool from Fluxim, was employed for capacitance-voltage (C-V) measurements and transient electroluminescence (EL) decay measurements.
The C-V measurements provided insights into the charge injection and recombination processes in the PeLEDs, indicating that the 25CC film (with both VitC and 18-Crown-6) had the highest charge transfer efficiency and lowest trap density.
Transient EL measurements revealed that the 25CC devices had the fastest response time and lowest trap density, confirming the superior carrier mobility and performance
Triple-junction perovskite–perovskite–silicon solar cells with power conversion efficiency of 24.4%
Hang Hu; An, Sophie X.; Li, Yang; Orooji, Seyedamir; Singh, Roja; Schackmar, Fabian; Laufer, Felix; Jin, Qihao; Feeney, Thomas; Diercks, Alexander; Gota, Fabrizio; Moghadamzadeh, Somayeh; Pan, Ting; Rienäcker, Michael; Peibst, Robby; Nejand, Bahram Abdollahi; Paetzold, Ulrich W.
Energy Environ. Sci.2024,17, 2800-2814.
In this paper Prof. Ulrich W. Paetzold's team at KIT achieved a record 24.4% efficiency in triple junction perovskite solar cells using a new vacuum-assisted growth process. The mid-subcell, made of FAPbI3, ensures thermal stability and ideal interfaces.
How Paios was used
The researchers used the PAIOS system for various measurements including electrical impedance spectroscopy, transient photovoltage, electroluminescence, photoluminescence imaging, Mott-Schottky, dark J–V curves, and space-charge-limited current, enabling efficient, streamlined analysis and characterization of their triple-junction perovskite solar cells .
Is Doping of Spiro-OMeTAD a Requirement for Efficient and Stable Perovskite Indoor Photovoltaics?
Sami Toikkonen, G. Krishnamurthy Grandhi, Shaoyang Wang, Bora Baydin, Basheer Al-Anesi, L. Krishnan Jagadamma, Paola Vivo.
Adv Devices Instrum.2024;5:0048.
The study investigates the necessity of doping Spiro-OMeTAD in lead halide perovskite (LHP) indoor photovoltaics (IPVs). It concludes that undoped Spiro-OMeTAD can achieve high efficiency and stability under low-light conditions, rivaling doped counterparts, suggesting that dopants may not be essential for effective IPV performance.
How Litos Lite was used
Litos Lite was utilized to perform J–V reverse and forward sweeps (scan rate 50 mV s−1), maximum power point (MPP) tracking, and stable power output (SPO) measurements on the prepared photovoltaic cells. These measurements were conducted under both simulated sunlight (AM 1.5G, 1-Sun, 100 mW cm−2) and indoor WLED illumination (5,000 lux, ≈1.60 mW cm−2) in N2 atmosphere. The indoor MPP tracking was performed either under continuous illumination or in 8-hour light–16-hour dark cycles .
How Paios was used
Transient photovoltage and transient photocurrent measurement were carried out with the all-in-one characterization platform, Paios.

Enhancing the Performance of 2D Tin-Based Pure Red Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes through the Synergistic Effect of Natural Antioxidants and Cyclic Molecular Additives
C.-H. Chen, M.-H. Yu, Y.-Y. Wang, Y.-C. Tseng, I. Chao, I. Ni, B.-H. Lin, Y.-J. Lu, C.-C. Chueh,
Small 2024, 2307774.
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202307774
This paper presents a method to significantly enhance the performance of 2D tin-based red perovskite LEDs through the use of natural antioxidants and cyclic molecular additives, particularly ascorbic acid and 18-Crown-6. These additives mitigate the oxidation of Sn2+ to Sn4+ and improve film quality, leading to a substantial increase in external quantum efficiency (EQE), purer color, and better bias stability. The study showcases a potential dual-additive approach for advancing 2D Sn-based perovskite LEDs towards sustainability and efficiency.
How Paios was used
Paios was utilized for comprehensive electrical characterization, including space-charge-limited current measurements, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, capacitance-voltage analysis, and transient electroluminescence studies. These tests revealed that the additives effectively reduced trap densities and leakage currents, improved carrier transport, and enhanced charge transfer efficiency, corroborating the additives' impact on device performance and stability.

Oxygen-Containing Diamine Cations Enable Highly Efficient and Stable 2D Dion-Jacobson Perovskite Solar Cells
Fangfang Yuan, Yuncai Liang, Zhipeng Miao, Ting Zhang, Rudai Zhao, Sihui Peng, Yunhang Xie, Wenlong Liang, He Zhu, Pengwei Li, Yiqiang Zhang, and Yanlin Song
Chemistry of Materials 2024 36 (3), 1621-1630
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c02960
This paper reports the development of highly efficient and stable 2D Dion-Jacobson perovskite solar cells using oxygen-containing diamine cations (OBEAI). These cations optimize charge transfer properties, leading to a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of up to 18.81% and outstanding stability, maintaining over 90% of initial performance after 2000 hours.
How Paios was used
Paios was used to assess the charge transport and recombination dynamics in perovskite films, highlighting improved electron transport, reduced recombination, and enhanced charge collection efficiency after OBEAI modification.

Electrochemical Doping Effect on the Conductivity of Melanin-Inspired Materials
Nayrim Brizuela Guerra, João Victor Morais Lima, Natan Luis Nozella, Miguel Henrique Boratto, João Vitor Paulin, and Carlos Frederico de Oliveira Graeff
ACS Applied Bio Materials Article ASAP
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.3c01166
This study explores increasing the conductivity of synthetic melanin derivatives through electrochemical doping, revealing that different anions can significantly affect charge transport. The most effective doping achieved with ClO4− anions, enhanced electronic transport to levels surpassing some reported melanin devices, suggesting a promising method for tuning melanin's conductivity for bioelectronics applications.
How Paios was used
Paios was employed for electrical characterizations before and after electrochemical treatments, allowing the investigation of charge transport and recombination dynamics. This contributed to understanding the improved photovoltaic performance due to enhanced electron transport and reduced recombination, crucial for developing efficient melanin-based devices.

Over 14% efficiency of highly reproducible Sn perovskite solar cell via defect passivation and morphology repairment
Zheng Zhang, Jiaqi Liu, Huan Bi, Liang Wang, Qing Shen, Shuzi Hayase,
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 483, 2024, 149345, ISSN 1385-8947,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.149345.
This study achieved over 14% efficiency in highly reproducible Sn perovskite solar cells by utilizing polysilanes, particularly polymethyl-phenyl-silane (PMPS), for defect passivation and morphology improvement. The application of PMPS enhanced surface quality, grain size, and reduced Sn4+ defects, leading to significant improvements in device efficiency and stability.
How Paios was used
Paios was used to evaluate charge transport and recombination dynamics, providing insights into the improved photovoltaic performance through enhanced electron transport, reduced recombination, and increased charge collection efficiency.

Achieving 19.4% organic solar cell via an in situ formation of p-i-n structure with built-in interpenetrating network
Ying Zhang, Wanyuan Deng, Christopher E. Petoukhoff, Xinxin Xia, Yongwen Lang, Hao Xia, Hua Tang, Hrisheekesh Thachoth Chandran, Sudhi Mahadevan, Kuan Liu, Patrick W.K. Fong, Yongmin Luo, Jiaying Wu, Sai-Wing Tsang, Frédéric Laquai, Hongbin Wu, Xinhui Lu, Yang Yang, Gang Li
Joule, 2024, , ISSN 2542-4351,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2023.12.009.
This study introduces a guest polymer-tailored layer-by-layer (GPT-LBL) method for creating organic solar cells (OSCs) with a p-i-n microstructure, improving vertical composition and molecular organization control. By monitoring pre-aggregation behaviors of non-fullerene acceptors, this approach enhances charge transport, reduces energy loss, and increases efficiency. A resulting GPT-LBL OSC demonstrated a remarkable power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 19.41% (certified 19.0%), and a large-area device showed a PCE of 17.52% using green-solvent processing, marking a significant advancement in scalable and environmentally friendly OSCs.
How Paios was used
Photo-CELIV measurements were carried out with Paios.

Enhancing the Performance of 2D Tin-Based Pure Red Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes through the Synergistic Effect of Natural Antioxidants and Cyclic Molecular Additives
C.-H. Chen, M.-H. Yu, Y.-Y. Wang, Y.-C. Tseng, I. Chao, I. Ni, B.-H. Lin, Y.-J. Lu, C.-C. Chueh,
Small 2024, 2307774.
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202307774
This research explores the use of natural antioxidants as additives to improve the fabrication of environmentally friendly Sn-based perovskite films, tackling oxidation and crystallization challenges. Ascorbic acid is highlighted for its effectiveness against oxidation, and when combined with 18-Crown-6, it enhances 2D red Sn-based PeLED performance, increasing efficiency, color purity, and stability, showcasing a sustainable dual-additive approach for optoelectronic applications.
How Paios was used
Impedance and TEL to demonstrate better transport with additives.

All inorganic CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells with reduced mobile ion concentration and film stress
Nguyen, H., Penukula, S., Mahaffey, M. et al. MRS Communications (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00510-7
This study investigates how polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) affects cesium-based lead halide perovskites, focusing on phase, morphology, film stress, and ion concentration during aging. Using PVP in CsPbI3 enhances film stability by inducing compressive stress, with negligible impact on bandgap and ion behavior under aging conditions.
How Paios was used
The all in one characterization tooll, Paios, was used to analyse ion concentration with transient current measurements.

D-A-D typed fused-ring perylene diimide: A cathode interface material for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells
Lei Gao, Helin Wang, Qiang Guo, Zongtao Wang, Fan Yuan, Erjun Zhou,
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 480, 2024, 148277, ISSN 1385-8947,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.148277.
The paper presents a novel D-A-D typed fused-ring perylene diimide (PDI)-based organic small molecule, PDTI1, as a cathode interface layer (CIL) for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells (PSCs). PDTI1 enhances electron transport, improves power conversion efficiency (PCE) to 24.64%, and offers better stability compared to control devices. This work demonstrates PDTI1's superiority as a CIL, providing an alternative for high-efficiency PSCs.
How Paios was used
Paios was used in the study for conducting two key tests: Transient Photocurrent (TPC) and Transient Photovoltage (TPV). These tests were performed in the dark to analyze the characteristics of the solar cells.

Efficiency-enhancement of lead-free ASnI2Br perovskite solar cells by phenyltrihydrosilane passivation effective for Sn4+ reduction and hydrophobization
Sota Kikuchi, Takayuki Okamoto, Mengmeng Chen, Shen Qing, Shuzi Hayase,
Next Materials, Volume 3, 2024, 100098, ISSN 2949-8228,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nxmate.2023.100098.
The paper presents a study on improving the efficiency of lead-free ASnI2Br perovskite solar cells using phenyltrihydrosilane (PhSiH3) passivation. This passivation effectively reduces Sn4+ and creates a hydrophobic surface, enhancing the solar cells' efficiency from 3.65% to 5.50%. The process involves passivating the film surface with PhSiH3 solution, which decreases Sn4+ concentration on the perovskite film surface and makes the surface hydrophobic, resulting in better contacts with the C60 layer. The study demonstrates the effectiveness of PhSiH3 treatment in enhancing solar cell performance.
How Paios was used
Paios was utilized specifically for impedance measurement and analysis. This all-in-one characterization tool helped the researchers in assessing the electrical properties of the perovskite solar cells, which is crucial for understanding and enhancing their performance.

Introducing back-surface field for efficient inverted CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells
hunyan Lu, Xiaodong Li, Haobo Yuan, Wenxiao Zhang, Xuemin Guo, Acan Liu, Hui Yang, Wen Li, Zhengbo Cui, YuYang Hu, Junfeng Fang,
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 480, 2024, 147267, ISSN 1385-8947,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.147267
The paper introduces a back-surface field in inverted CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells using 4-Imidazoleethylamine (4-IEA) treatment to improve efficiency and stability. The treatment upshifts the Fermi level at the CsPbI3 surface, creating an extra back-surface field that aligns with the built-in potential of the solar cells. This alignment reduces energy loss and facilitates electron extraction at the CsPbI3/electron transporting layer interface. Additionally, 4-IEA passivates interfacial defects due to its Lewis base-acid interaction with CsPbI3. The result is a power conversion efficiency of 20.22% and good operational stability, retaining over 70% efficiency after 200 hours at 65℃.
How Paios was used
Paios was employed for transient photocurrent decay (TPC) and transient photovoltage (TPV) decay measurements. These measurements were crucial in understanding the dynamic charge transport process in the solar cells. The TPC and TPV results demonstrated a significant reduction in non-radiative recombination and improved charge transport efficiency in the cells treated with 4-IEA, contributing to the overall improved performance of the solar cells.
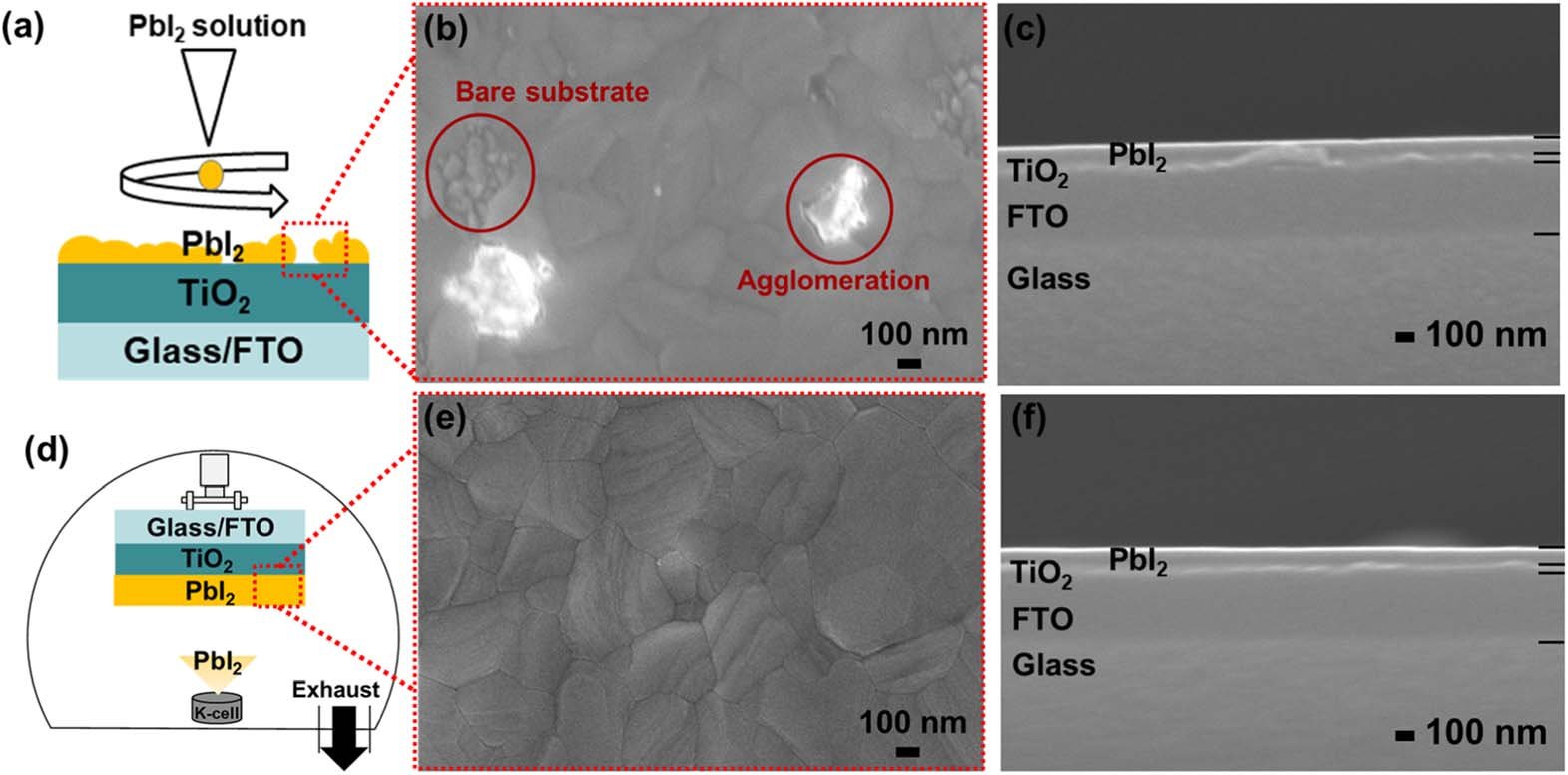

Thermal evaporated PbI2 enables high-quality perovskite films and improves their solar cell performance
Munkhtuul Gantumur et al 2024 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 63 015501
The study in "Japanese Journal of Applied Physics" by Munkhtuul Gantumur et al. explores the use of vacuum-deposited PbI2 to enhance the quality of perovskite films in solar cells. This method significantly improves the film's quality compared to spin-coated PbI2, leading to higher power conversion efficiency and better thermal stability in perovskite solar cells. Vacuum-deposited PbI2 results in uniform, pinhole-free films, facilitating efficient intercalation of MAI and the formation of high-quality MAPbI3 perovskite layers. This method also reduces ion migration, contributing to the improved performance and stability of the solar cells.
How Paios was used
Paios was used for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to examine the perovskite solar cells (PSCs). This technique provided insights into the electrical properties of the cells, such as resistance and capacitance, which are crucial for understanding and improving their performance.

Tissue Equivalent Curved Organic X-ray Detectors Utilizing High Atomic Number Polythiophene Analogues
M. P. A. Nanayakkara, Q. He, A. Ruseckas, A. Karalasingam, L. Matjacic, M. G. Masteghin, L. Basiricò, I. Fratelli, A. Ciavatti, R. C. Kilbride, S. Jenatsch, A. J. Parnell, B. Fraboni, A. Nisbet, M. Heeney, K. D. G. I. Jayawardena, S. R. P. Silva, Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304261. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202304261
his paper focuses on the development of tissue-equivalent organic X-ray detectors using high atomic number polythiophene analogues, achieving high sensitivity and flexibility.
How Paios was used
Paios was used to analyze charge transport processes, providing insights into the mobility-lifetime product of the materials, crucial for understanding and improving the performance of the X-ray detectors.

Inhibition of Sn2+ Oxidation in FASnI3 Perovskite Precursor Solution and Enhanced Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells by Reductive Additive
Md. Abdul Karim, Kiyoto Matsuishi, Md. Emrul Kayesh, Yulu He, and Ashraful Islam
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2023 15 (39), 45823-45833
This paper discusses the improvement of FASnI3 perovskite solar cells' reproducibility and stability by incorporating 4F-PHCl, a reductive molecule, in the perovskite precursor solution. 4F-PHCl enhances the solution's stability, prevents Sn2+ oxidation, and improves the films' crystallinity and stoichiometry, resulting in a power conversion efficiency of 10.86%.
How Paios was used
PAIOS was used to measure transient photovoltage and photocurrent decays, shedding light on charge carrier dynamics and demonstrating improved charge transport and reduced recombination in 4F-PHCl-treated devices.

Surface Modulation via Conjugated Bithiophene Ammonium Salt for Efficient Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
Xin Zhang, Stijn Eurelings, Andrea Bracesco, Wenya Song, Stijn Lenaers, Wouter Van Gompel, Anurag Krishna, Tom Aernouts, Laurence Lutsen, Dirk Vanderzande, Mariadriana Creatore, Yiqiang Zhan, Yinghuan Kuang, and Jef Poortmans
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2023 15 (40), 46803-46811
This paper investigates enhancing perovskite solar cells' efficiency and stability using bi-TPAI surface modulation. It significantly improves power conversion efficiency and operational stability by passivating surface defects and facilitating charge extraction.
How Paios was used
Paios was employed for transient photocurrent and photovoltage measurements, revealing optimized charge dynamics and reduced recombination, which contribute to the observed performance improvements.

Over 19% Efficiency in Ternary Organic Solar Cells Enabled by n‑Type Dopants
Zhaoheng Ling, Mohamad Insan Nugraha, Wisnu Tantyo Hadmojo, Yuanbao Lin, Sang Young Jeong, Emre Yengel, Hendrik Faber, Hua Tang, Frédéric Laquai, Abdul-Hamid Emwas, Xiaoming Chang, Temur Maksudov, Murali Gedda, Han Young Woo, Iain McCulloch, Martin Heeney, Leonidas Tsetseris, and Thomas D. Anthopoulos
ACS Energy Letters 2023 8 (10), 4104-4112
DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c01254
This study explores the use of ethyl viologen (EV) and methyl viologen (MV) as n-type dopants in organic photovoltaics (OPVs). Incorporating these dopants into a ternary blend significantly improves OPV performance, with PCEs up to 19.03%. EV and MV enhance microstructure and absorption, balance carrier mobility, and reduce recombination, offering a promising route for advanced OPV efficiency.
How Paios Was used
In the study, Paios from Fluxim was employed for various measurements in both steady-state and transient modes. Specifically, it was used for Transient Photo-Voltage (TPV) measurements to observe photovoltage decay under small optical perturbations and various light-intensity biases. This helped in analyzing bimolecular charge carrier recombination. Additionally, Photo-CELIV measurements and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) were conducted using PAIOS, the latter under an open circuit voltage in the dark across a frequency range of 3 MHz to 300 Hz

Ferrocene Derivatives for Improving the Efficiency and Stability of MA-Free Perovskite Solar Cells from the Perspective of Inhibiting Ion Migration and Releasing Film Stress
H. Bi, J. Liu, Z. Zhang, L. Wang, G. Kapil, Y. Wei, A. Kumar Baranwal, S. Razey Sahamir, Y. Sanehira, D. Wang, Y. Yang, T. Kitamura, R. Beresneviciute, S. Grigalevicius, Q. Shen, S. Hayase, Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304790. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202304790
This paper investigates enhancing the efficiency and stability of MA-free perovskite solar cells using a ferrocene derivative (DBzFe) additive. The additive improves film quality, passivates defects, and inhibits ion migration, achieving a high power conversion efficiency of 23.53%.
How Paios was used
Paios was utilized for Mott-Schottky analysis and temperature-dependent c-f curves, providing insights into charge carrier dynamics, energy barriers for ion migration, and the benefits of DBzFe in improving device performance and stability.

RbPbI3 Seed Embedding in PbI2 Substrate Tailors the Facet Orientation and Crystallization Kinetics of Perovskites
G. Yu, Y. Huang, D. Khan, Y. Sui, S. Wang, X. Yang, W. Zhou, K. Chang, J. Tang, W. Chen, P. Han, Z. Tang, Small 2023, 2307219. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202307219
The paper explores the impact of embedding RbPbI3 seeds in PbI2 substrates to tailor the facet orientation and crystallization kinetics of perovskites, improving the performance and durability of perovskite solar cells.
How Paios was used
Paios was used for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, revealing enhanced carrier dynamics and reduced non-radiative recombination in seed-processed films, contributing to the cells' high efficiency and long-term stability.

A series of perylene diimide cathode interlayer materials for green solvent processing in conventional organic photovoltaics
Wolfe, K. M.; Alam, S.; German, E.; Alduayji, F. N.; Alqurashi, M.; Laquai, F.; Welch, G. C. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1620–1629. doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.119
The paper focuses on developing and implementing new cathode interlayer (CIL) materials based on N-annulated perylene diimides in organic photovoltaic devices, aiming for efficient and environmentally friendly solar cells.
How was Paios used
PAIOS was used to measure transient photocurrent and light intensity-dependent IV measurements, confirming efficient charge extraction and minimal recombination within the device, contributing to the understanding and optimization of these new CIL materials for improved solar cell performance.

Dual Interfacial Tin-Oxide Layer with Chloride Salt for High- Performance and Durable Perovskite Solar Cells
Sasiphapa Rodbuntum, Nuttaya Sukgorn, Narong Chanlek, Hideki Nakajima, Nopporn Rujisamphan, Pipat Ruankham, Duangmanee Wongratanaphisan, Anusit Kaewprajak, and Pisist Kumnorkaew
ACS Applied Energy Materials 2023 6 (20), 10364-10375
The paper addresses enhancing perovskite solar cells' performance and stability using a dual interfacial tin-oxide layer with chloride salt. It achieved a high power conversion efficiency and remarkable operational stability over 2400 hours.
How Paios was used
Paios was utilized for electrical and optical characterization, particularly for electrical impedance spectroscopy and intensity-modulated photocurrent spectroscopy measurements, providing insights into charge transport and recombination dynamics at the device interfaces.

Charge injection engineering at organic/ inorganic heterointerfaces for high-efficiency and fast-response perovskite light-emitting diodes
Li, Z., Chen, Z., Shi, Z. et al. Nat Commun 14, 6441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41929-9
This paper focuses on enhancing the performance and response speed of perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) by engineering the charge injection at the organic-inorganic heterointerfaces. They introduced a self-assembled monolayer to improve interface robustness, passivate interfacial traps, and align energy levels.
How Paios was used
Paios was used to study the transient photo-voltage and photocurrent responses, revealing improved charge injection and transport properties, which significantly enhanced the device's efficiency and response speed.

Fluorescent Conversion Agent Embedded in Zinc Oxide as an Electron-Transporting Layer for High-Performance Non-Fullerene Organic Solar Cells with Improved Photostability
J. Chen, G. Zhang, Z. Chen, J. Xiao, T. Xia, X. Li, H.-L. Yip, Small 2023, 2306471.
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202306471
The study enhances organic solar cells' performance and photostability by incorporating a fluorescent conversion agent, CBS, into the ZnO electron-transporting layer. This innovative hybrid ETL boosts power conversion efficiencies and shields active layers from UV-induced degradation.
How Paios was used
Paios was employed to measure transient photocurrents, illuminating the charge extraction process and demonstrating improved charge transport and reduced recombination in devices with the ZnO:CBS ETL.

Thermally-Induced Degradation in PM6:Y6-Based Bulk Heterojunction Organic Solar Cells
S. Alam, H. Aldosari, C. E. Petoukhoff, T. Váry, W. Althobaiti, M. Alqurashi, H. Tang, J. I. Khan, V. Nádaždy, P. Müller-Buschbaum, G. C. Welch, F. Laquai
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2308076. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202308076
This paper investigates the impact of thermal annealing on PM6:Y6-based organic solar cells, focusing on performance degradation due to structural and morphological changes at elevated temperatures. It finds that VOC and FF significantly decrease with annealing above 140°C due to altered charge transport and extraction.
How Setfos was used
Using SETFOS software, the study simulates device performance, correlating optical-electrical properties with device parameters to understand the degradation mechanisms and guide future improvements.
How Paios was used
Paios was used to measure transient photocurrent, photo-voltage, and charge extraction properties, providing insights into charge generation, recombination, and extraction mechanisms, helping to understand the performance drop at elevated annealing temperatures.

Drift-Diffusion Simulations of Charge Transport and Trap Dynamics in Organic Semiconductor Materials
Dr. Camilla Arietta VAEL-GARN
Ph. D Thesis, EPFL , 12 Sept. 2023
https://doi.org/10.5075/epfl-thesis-10350
The study explores polymeric semiconductors in organic electronics, using drift-diffusion simulation to study three areas. First, the applicability of thermally stimulated current measurement for studying trap states in organic semiconductors is investigated, identifying a reliable formula for data analysis. Second, reversible trap states in a polymeric light-emitting diode are studied, suggesting trap state formation and disaggregation may involve water and oxygen molecules. Lastly, the operational principles of an upconverter device converting near infra-red to visible light are examined, finding that electron mobility in the emission layer significantly affects the device's response time.

Enhancement of Efficiency and Stability for Tin Halide Perovskite Solar Cells by Using Improved Doping Method
Zhang, Z., Wang, L., Bi, H., Baranwal, A. K., Kapil, G., Sanehira, Y., Liu, J., Liu, D., Shen, Q., Hayase, S.,
Adv. Optical Mater. 2023, 2300962.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202300962
To enhance the efficiency of tin halide perovskite solar cells (PKSCs), researchers addressed defects like Sn4+ and iodide vacancies by introducing copper iodide (CuI) doping. A preprocessing method for CuI improved perovskite layer quality, resulting in efficiency increases from 9.8% to 13.1% for P-I-N structures and 9.4% to 10.5% for hole transport layer (HTL)-free structures. These doped tin-PKSCs also exhibited improved stability, retaining 75% of their initial power conversion efficiency after 102 days of storage.
How Paios was used
Intensity-modulated photovoltage spectroscopy (IMVS), Intensity-modulated photovoltage spectroscopy (IMPS), Transient photovoltaic voltage (TPV), and Transient photovoltaic current (TPC) were carried out via PAIOS software.

Manipulation of the Structure and Optoelectronic Properties through Bromine Inclusion in a Layered Lead Bromide Perovskite
Lin-jie Yang, Wenye Xuan, David Webster, Lethy Krishnan Jagadamma, Teng Li, David N. Miller, David B. Cordes, Alexandra M. Z. Slawin, Graham A. Turnbull, Ifor D. W. Samuel, Hsin-Yi Tiffany Chen, Philip Lightfoot, Matthew S. Dyer, and Julia L. Payne
Chemistry of Materials 2023 35 (10), 3801-3814
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c03125
This study demonstrates the tunability of organic-inorganic metal halides through anion substitution, incorporating bromine into [H3N(CH2)6NH3]PbBr4 to create [H3N(CH2)6NH3]PbBr4·Br2. This inclusion of molecular bromine leads to a reduced band gap, structural phase transition, and improved carrier mobility. The key to this manipulation is the formation of halogen bonds between Br2 and Br in the [PbBr4]∞ layers. This work opens possibilities for tuning electronic properties in layered organic-inorganic perovskites and represents the first example of molecular bromine inclusion in such a material.
How Paios was used
The current−voltage measurements were carried out using the all-in-one characterization platform Paios, Fluxim AG, Switzerland. The voltage scan range used was 0−9 V.

Heat Soaking for Improving Rollover From S at the Back of CIGSSe Solar Cells
J. H. Siew, Y. -H. Chen, Y. -L. Chang, C. -H. Lai and T. -Y. Lin,
IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 503-509, July 2023,
doi: 10.1109/JPHOTOV.2023.3271891.
Researchers investigated a low-temperature heat-soaking (HS) treatment to mitigate the rollover effect in copper indium gallium sulfur selenide (CIGSSe) solar cells. Excessive sulfur accumulation on the absorber's backside forms a Schottky barrier, causing current-voltage rollover. HS treatment reduced saturation and improved cell efficiency by over 6%. Elemental redistribution after HS reduced sulfur accumulation, enabling Fowler-Nordheim tunneling through a shortened Schottky barrier width. This study offers a simple, practical strategy to address the second reverse diode effect caused by sulfurization in CIGSSe solar cells.
How Paios was used
Temperature-dependent dark current density and voltage were measured using a Paios system with Fluxim Characterization Suite software attached to a temperature-controlled probe stage.

Interface-Engineered Organic Near-Infrared Photodetector for Imaging Applications
Abu Bakar Siddik, Epimitheas Georgitzikis, Yannick Hermans, Jubin Kang, Joo Hyoung Kim, Vladimir Pejovic, Itai Lieberman, Pawel E. Malinowski, Andriy Kadashchuk, Jan Genoe, Thierry Conard, David Cheyns, and Paul Heremans
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2023 15 (25), 30534-30542
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c03708
This study presents a high-speed, low dark current near-infrared organic photodetector (NIR OPD) on a silicon substrate using amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide (a-IGZO) as the electron transport layer (ETL). Detailed characterization reveals the dark current mechanism as trap-assisted field-enhanced thermal emission, significantly reduced by introducing an interfacial layer. The NIR OPD achieves a low dark current of 125 pA/cm² at -1 V reverse bias and boasts a rapid photo response time, making it suitable for high-quality sample image capture in an imager on a complementary metal oxide semiconductor read-out circuit.
How Paios was used
Q-DLTS and TPV decay measurements were performed using Paios.

Robust and Manufacturable Lithium Lanthanum Titanate-Based Solid-State Electrolyte Thin Films Deposited in Open Air
Mohammed Sahal, Jie Molloy, Venkateshwaran Ravi Narayanan, Leila Ladani, Xiaochuan Lu, and Nicholas Rolston
ACS Omega 2023 8 (31), 28651-28662
Researchers have developed a high-throughput, one-minute process for printable thin-film ceramic solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) called "Robust LLTO" (R-LLTO). R-LLTO exhibits excellent mechanical properties, with flexibility, low modulus (~35 GPa), and high fracture toughness (>2.0 MPa m). This opens new design possibilities for robust solid-state batteries with improved energy density and processability compared to traditional SSEs.
How Paios was used
The complex impedance response of the inplane configuration was measured using a Paios measurement system (Fluxim AG) by varying the frequency from 10 Hz to 10 MHz for an applied voltage with an amplitude of 50 mV. Data from EIS measurements were fitted with simulated response of equivalent circuits using Fluxim’s Characterization Suite software.

Efficiency and stability improvement of non-fullerene organic solar cells with binary anode buffer layer
Zhou, X., Yan, Y., Zhang, F. et al.
J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1415 (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10838-4
To enhance the performance and stability of organic solar cells (OSCs), a binary anode buffer layer strategy was employed using molybdenum oxide (MoO3) and PEDOT:PSS. This improved work function and interface contact, increasing the power conversion efficiency (PCE) from 16.25% to 17.34%. Additionally, MoO3 prevented direct contact between PEDOT:PSS and ITO, enhancing device stability. This approach offers a simple and efficient method for high-efficiency, stable OSCs suitable for commercial applications.

Benchmarking the performance of lithiated metal oxide interlayers at the LiCoO2|LLZO interface
Andre Müller, Faruk Okur,ab Abdessalem Aribia, Nicolas Osenciat, Carlos A. F. Vaz, Valerie Siller, Mario El Kazzi, Evgeniia Gilshtein, Moritz H. Futscher, Kostiantyn V. Kravchyk, Maksym V. Kovalenko and Yaroslav E. Romanyuk
Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 2138-2146
Integrating Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) solid-state electrolytes with high-energy cathodes in all-solid-state batteries faces challenges due to diffusion and solid-state reactions at the cathode-electrolyte interface during fabrication. This study explores lithiated Nb, Al, and Ti metal oxide interlayers as diffusion barriers to enhance Li-ion transfer between LiCoO2 and LLZO. These interlayers reduce interfacial impedance from 8 kΩ cm² to 1 kΩ cm², improving battery performance. Li-Nb-O interlayer stands out, delivering the highest discharge capacities.
How Paios was used
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic measurements were performed between 5 MHz and 1 Hz with an AC amplitude of 50 mV using Paios.

A donor–acceptor-type hole-selective contact reducing non-radiative recombination losses in both subcells towards efficient all-perovskite tandems
Zhu, J., Luo, Y., He, R. et al.
Nat Energy 8, 714–724 (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01274-z
A donor-acceptor molecule, 2F, serves as a hole-selective contact for both wide-bandgap (WBG) and low-bandgap (LBG) perovskite subcells in all-perovskite tandem solar cells. In the WBG cell, 2F extracts holes efficiently and minimizes recombination losses by passivating defects. In the LBG cell, 2F suppresses losses, enhances film quality, and regulates crystal growth. This results in WBG and LBG devices with efficiencies of 19.33% and 23.24%, respectively, contributing to a monolithic all-perovskite tandem solar cell with an efficiency of 27.22%.
How Paios was used
Transient photovoltage (TPV), transient photocurrent (TPC), Mott–Schottky plots and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were performed using the all-in-one characterization system Paios from Fluxim.

Morphology control by tuning electrostatic interactions for efficient polythiophene-based all-polymer solar cells
Ma et al.,
solar cells, Chem (2023),
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2023.04.021
Polythiophenes, while cost-effective, lag behind in organic solar cells. Researchers studied polythiophene:polymer acceptor (PY-IT) interactions, highlighting the role of electrostatic forces. Introducing electron-withdrawing groups to P3HT reduced intermolecular interactions, improving blend miscibility. This led to a record-high 15.3% power conversion efficiency in PDCBT, advancing polythiophene-based all-polymer solar cells for practical use.

Multi-Site Intermolecular Interaction for In Situ Formation of Vertically Orientated 2D Passivation Layer in Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
Liu, L., Tang, J., Li, S., Yu, Z., Du, J., Bai, L., Li, X., Yuan, M. and Jiu, T. (2023),
Adv. Funct. Mater., 33: 2303038.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202303038
To enhance perovskite solar cell (PSC) performance, surface passivation using 2D perovskite is crucial, but random orientation hinders carrier transport. A surface passivation layer with multiple nitrogen sites from the organic spacer molecule PAH is introduced on FAPbI3 perovskite. Through interactions with PbI2, PAH effectively passivates FAPbI3 defects, with 2D nanosheets growing perpendicularly for improved charge transfer. This achieves an impressive 24.6% efficiency and excellent long-term stability, offering insights into designing efficient and stable PSCs with novel organic halide salts.
How Paios was used
The TPC/TPV decays were recorded via all-in-one characterization platform Paios.

Thin-film image sensors with a pinned photodiode structure
Lee, J., Georgitzikis, E., Hermans, Y. et al.
Nat Electron 6, 590–598 (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-023-01016-9
Thin-film image sensors with pinned photodiode structures, using organic or colloidal quantum dot photodiodes, demonstrate noise performance comparable to silicon-based counterparts. These sensors exhibit low noise, reduced dark current, high capacity, and efficient electron-to-voltage conversion. For instance, an organic absorber-based sensor achieves 54% quantum efficiency at 940 nm with 6.1e– read noise.
How Paios was used
The transient photoresponse, photocurrent linearity and capacitance–voltage measurements were performed using a Paios all-in-one system by Fluxim.

Multifunctional and multi-site interfacial buffer layer for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
Pengyu Su, Huan Bi, Du Ran, Li Liu, Wenjing Hou, Guangzhao Wang, Wenbing Shi,
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 472, 2023, 145077, ISSN 1385-8947,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145077
In a bid to enhance perovskite solar cell (PSC) performance and stability, a novel interfacial buffer layer called Ethyl p-nitrobenzoate (EPN) was introduced. EPN improved film quality, reduced defect density, relieved interfacial stress, and suppressed nonradiative recombination at the interface. This innovation led to a high 23.16% power conversion efficiency and improved device stability, showcasing the potential of multifunctional interfacial buffer layers in high-performance PSCs.
How Paios was used
TPC, TPV, IMPS, IMVS, and built-in potential were carried out via PAIOS in the structure of ITO/SnO2/(EPN)/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag, and the results were fitted using the companion software of PAIOS.

Vacuum deposited organic solar cells with BTIC-H as A–D–A non-fullerene acceptor
Irfan Habib, Pascal Kaienburg, Dondong Xia, Olivia Gough, Ming Zhu, Joseph Spruce, Weiwei Li, Moritz Riede;
APL Mater. 1 June 2023; 11 (6): 061128.
https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0148208
The power conversion efficiency of solution-processed organic solar cells (OSCs) nearly doubled when non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs) replaced fullerene derivatives. However, this transition hasn't fully occurred in vacuum-thermal evaporated (VTE) OSCs because most NFAs are too large to evaporate without damage. We've fabricated VTE OSCs using BTIC-H, a smaller NFA, and observed promising results, highlighting the potential for high-performance VTE NFAs in OSCs.
How Paios was used
Open-circuit corrected charge carrier extraction was performed with Paios from Fluxim AG, Switzerland. The 60 nmthick BHJ samples were illuminated with a white LED light for 100 μs until a steady-state Voc was reached. Delay times were varied between a few μs and 1 ms. The linear voltage pulse (ramp rate of 200 and 400 V/ms) was chosen long enough (∼30 μs) such that all mobile carriers were extracted, and the current peak decayed to the displacement current obtained from a dark measurement with no offset voltage applied.

Enabling Scalable, Ultralow-Voltage Flexible Organic Field-Effect Transistors via Blade-Coated Cross-Linked Thick Polyvinyl Alcohol Gate Dielectric
H. Fu, J. Peng, L. Xiang, Q. Zhang, X. Tan and Y. Lei,
IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 3239-3244, June 2023,
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10098909
A scalable, low-voltage flexible organic field-effect transistor (OFET) design utilizes blade-deposited thick cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol (c-PVA) dielectric to achieve <1V operation, nearly 10 cm²/V·s mobility, and excellent mechanical stability, making it ideal for cost-effective high-performance, low-voltage flexible OFET manufacturing in organic electronics.
How Paios was used
The capacitance and impedance spectra were recorded by the all-in- one measurement platform Paios.
Unraveling segregation behavior of inactive secondary phase driven by ion-competition reaction for perovskite-2D PbI2 heterojunction solar cells
Yajie Cheng, Junjie Ma, Huaiqing Luo, Meng Cai, Tangyue Xue, Guanghui Yu, Ziqiu Ren, Yanlin Song, Shou Peng, Yiqiang Zhang,
Nano Energy, Volume 115, 2023, 108690, ISSN 2211-2855,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108690
This study addresses the issue of undesirable segregation of inactive secondary phases in perovskite films, which negatively impacts charge-carrier transport and stability. The research delves into the chemical reactions and structural relationships responsible for this behavior. By converting the photoactive phase into an inactive one, a high-quality perovskite-PbI2 heterojunction film is created, improving carrier dynamics and achieving remarkable light resistance. The resulting perovskite solar cells reach an impressive efficiency of 24.23%. This work offers valuable insights into designing crystal structures for high-quality perovskite heterojunction devices.
How Paios was used
EIS, TPC, TPV, and capacitance-voltage (C-V) measurements were performed by Paios from Fluxim

Efficiency Enhancement of Wide Bandgap Lead Perovskite Solar Cells with PTAA Surface-Passivated with Monomolecular Layer from the Viewpoint of PTAA Band Bending
Huan Bi, Jiaqi Liu, Raminta Beresneviciute, Daiva Tavgeniene, Zheng Zhang, Liang Wang, Gaurav Kapil, Chao Ding, Shahrir Razey Sahamir, Yoshitaka Sanehira, Ajay Kumar Baranwal, Takeshi Kitamura, Dandan Wang, Yuyao Wei, Yongge Yang, Dong-Won Kang, Saulius Grigalevicius, Qing Shen, and Shuzi Hayase
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2023 15 (35), 41549-41559
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c08655
This research focuses on enhancing the efficiency of wide bandgap lead halide perovskite solar cells (WBG Pb-PVK PSCs) using FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2 as the light-harvesting layer. By passivating the hydrophobic surface of the hole transporting layer (PTAA) with a monomolecular layer, improved hydrophilicity and band alignment result in WBG Pb-PVK PSCs achieving an impressive 16.52% efficiency at 1.77 eV.
How Paios was used
MS curves, EIS, TPC, and TPV results were all performed using Paios from Fluxim
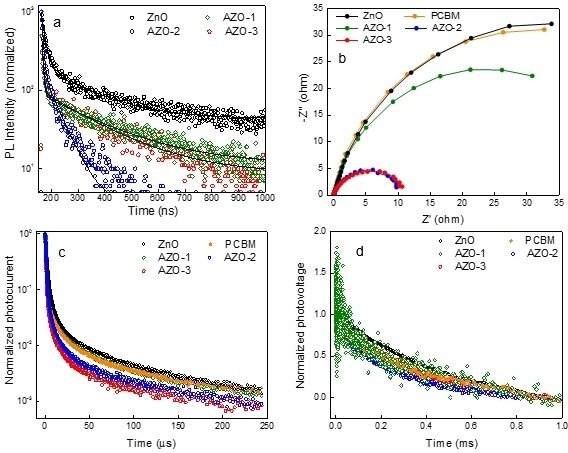
Interfacial Engineering of a PCBM/AZO Electron Transport Bilayer for Efficient and Stable Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
Ali, U., Javed, S., Qureshi, A. A., Akram, M. A.,
Chem Nano Mat 2023, 9, e202300175.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202300175
This research discusses the use of an interlayer of aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) nanoparticles to suppress interfacial recombination and improve the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells. The PCBM/AZO electron transport bilayer with an optimal concentration of 2% Al dopant exhibited greatly improved power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 18.63%, VOC of 1.13 V, and FF of 73% with negligible hysteresis index of 0.04.
How Paios was used
The TPC, TPV, and impedance measurements were performed using PAIOS from Fluxim. A pulse intensity for an optimized period was used to induce a spike in photovoltage and photo-current subsequently. The impedance spectra were taken from PAIOS v. 4.4 software, and scans were taken from 10 Hz to 2 MHz at a 0 V bias in the dark.

Perovskite Solar Cells Consisting of PTAA Modified with Monomolecular Layer and Application to All-Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells with Efficiency over 25%
Bi, H., Fujiwara, Y., Kapil, G., Tavgeniene, D., Zhang, Z., Wang, L., Ding, C., Sahamir, S. R., Baranwal, A. K., Sanehira, Y., Takeshi, K., Shi, G., Bessho, T., Segawa, H., Grigalevicius, S., Shen, Q., Hayase, S.,
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300089.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202300089
This research discusses the enhancement of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) by modifying the hole transport layer (HTL) with a monomolecular layer (MNL). The researchers focused on improving the efficiency of wide bandgap perovskite solar cells used in perovskite/perovskite tandem solar cells. They found that surface-modifying PTAA (poly[bis(4-phenyl)(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)amine]) with MNL improved PSC efficiency by enhancing perovskite film quality, reducing distortion, and decreasing charge recombination sites. The length of the alkyl group in the MNL also influenced the efficiency of the PTAA layer. The PTAA/monomolecular bilayer achieved a power conversion efficiency of 16.57% in wide bandgap lead PSCs. Furthermore, the PTAA/monomolecular substrate enabled all-perovskite tandem solar cells with over 25% efficiency. These findings demonstrate the potential of MNL modification for improving perovskite solar cell efficiency.
How Paios was used
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), Transient photovoltaic voltage (TPV), and Transient photovoltaic current (TPC) were carried out using Paios with an LED light.
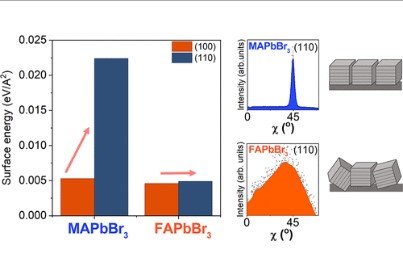
Solvent and A‑Site Cation Control Preferred Crystallographic Orientation in Bromine-Based Perovskite Thin Films
Juanita Hidalgo, Yu An, Dariia Yehorova, Ruipeng Li, Joachim Breternitz, Carlo A.R. Perini, Armin Hoell, Pablo P. Boix, Susan Schorr, Joshua S. Kretchmer, and Juan-Pablo Correa-Baena
Chemistry of Materials 2023 35 (11), 4181-4191
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c00075
This scientific article investigates the factors that determine crystallographic orientation in lead bromide perovskites. The researchers show that the solvent and organic A-site cation play a critical role in preferred orientation of the thin films. The results reveal that the solvent, specifically dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), influences the early stages of crystallization and induces preferred orientation by preventing colloidal particle interactions. Additionally, the choice of A-site cation, such as methylammonium or formamidinium, affects the degree of preferred orientation. Density functional theory calculations suggest that the difference in surface energy between the (100) and (110) facets is the reason for the varying degrees of preferred orientation. Besides, the researchers observe that the choice of A-site cation impacts ion density and accumulation, leading to increased hysteresis in solar cells. Overall, this study highlights the importance of solvent and A-site cation in determining crystallographic orientation and its impact on the electronic and ionic properties of solar cells.
How Litos Lite & Paios were used
LITOS LITE was used to measure the current density-voltage (J-V) characteristics of the solar cells. The J-V curves were obtained by scanning voltage in the range from 1.4 to -0.5 V with a scan speed of 50 mV·s-1 first in reverse and then in forward scan directions. The active area of the device was 0.128 cm2, and a black metal mask with an aperture area of 0.0625 cm2 was used to define the illuminated area.
Impedance Spectroscopy: #PAIOS was used to perform Impedance Spectroscopy (IS) on complete solar cells at room temperature under one sun illumination and in ambient air. The measurements were performed at five different offset voltages spaced from 0 V to the open circuit.
P3HT vs Spiro-OMeTAD as a hole transport layer for halide perovskite indoor photovoltaics and self-powering of motion sensors
Shaoyang Wang et al 2023 J. Phys. Mater. 6 024004
Indoor photovoltaic devices using halide perovskites are studied for their potential in powering IoT applications. CH3NH3PbI3-based devices with Spiro-OMeTAD and P3HT as hole transport layers were compared, and Spiro-OMeTAD showed higher power conversion efficiency. The best-performing Spiro-OMeTAD device successfully powered a wearable motion sensor, demonstrating the potential for self-sufficient sensor systems.
Light intensity-dependent J-V measurement, transient photovoltage (TPV) and transient photocurrent (TPC) measurement were carried out with the characterization platform, Paios, Fluxim AG, Switzerland.
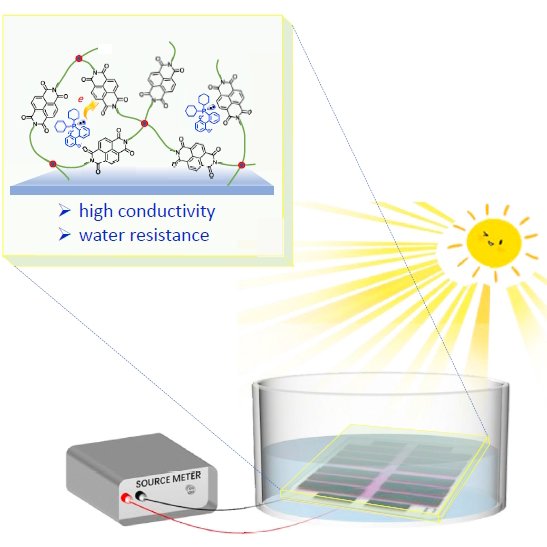
Robust and hydrophobic interlayer material for efficient and highly stable organic solar cells
Yi Yang, Jingwen Wang, Yunfei Zu, Qing Liao, Shaoqing Zhang, Zhong Zheng, Bowei Xu, Jianhui Hou,
Robust and hydrophobic interlayer material for efficient and highly stable organic solar cells,
Joule, Volume 7, Issue 3, 2023, Pages 545-557, ISSN 2542-4351,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2023.02.013
A robust, hydrophobic electron transporting interlayer for organic solar cells (OSCs) is designed using a cross-linkable naphthalene diimide (NDI) derivative. The non-polar electron donor PCy2 is used to n-dope the crosslinked c-NDI:PCy2 film, increasing its doping density and conductivity.
This hydrophobic interlayer protects the device against water, resulting in excellent water resistance. With the c-NDI:PCy2 interlayer, a power conversion efficiency of 17.7% is achieved, which is the highest for OSCs with an inverted device architecture. Notably, this OSC can be used underwater, maintaining 70% of its initial efficiency after 1,000 hours in the dark or 4 hours under continuous illumination.
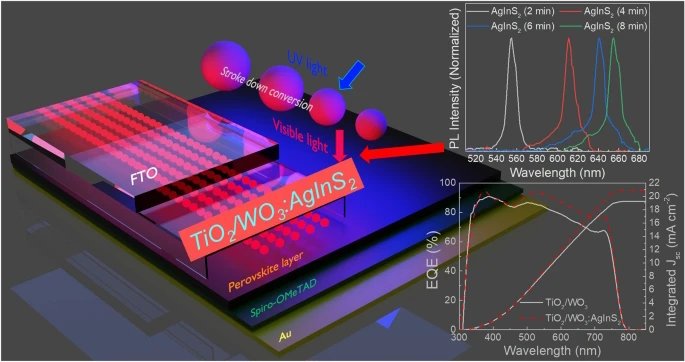
WO3:AgInS2 quantum dot electron transport layers in enhanced perovskite solar cells
Seriwattanachai, C., Kaewprajak, A., Sukgorn, N. et al.
Journal of Materials Research (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-00967-1
This study developed dual electron transport layers (TiO2/WO3:AgInS2 QDs) for planar perovskite solar cells, which improved charge extraction and transportation. AgInS2 quantum dots were fabricated with varying sizes, resulting in a redshift in the photoluminescence (PL) peak intensity.
The addition of AgInS2 QDs quenched the PL intensity of the perovskite film. Improved device stability was achieved due to the WO3:AgInS2 QDs layer, which protected the perovskite interface from direct contact with TiO2 and prevented UV decomposition. The TiO2/WO3:AgInS2 QDs electron transport layers enhanced the performance and long-term stability of perovskite solar cells.
The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), intensity modulated photovoltage spectroscopy (IMVS) and intensity modulate photocurrent spectroscopy (IMPS) were measured by PAIOS.
High-Performing Quasi-2D Perovskite Photodetectors with Efficient Charge Transport Network Built from Vertically Orientated and Evenly Distributed 3D-Like Phases
Li, B., Huang, X., Wu, X., Zuo, Q., Cao, Y., Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Xu, Y., Zheng, G., Chen, D., Zhu, X.-H., Huang, F., Zhen, H., Hou, L., Qing, J., Cai, W., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2300216. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202300216
Q-2D perovskites are promising photodetector materials, but their charge transport is limited by their hybrid low-dimensional structure. Researchers used a double-hole transport layer (PTAA & PEDOT:PSS) to create evenly-distributed 3D-like phases with vertical orientation, improving charge transport and reducing recombination.
This Ruddlesden-Popper perovskite photodetector achieved a high responsivity, specific detectivity, linear dynamic range, and fast rise/fall times. The study reveals the relationship between Q-2D perovskites' phase structure and performance, guiding future photodetector designs.
Transient photovoltage decay (TPV) measurements were performed with PAIOS instrumentation.
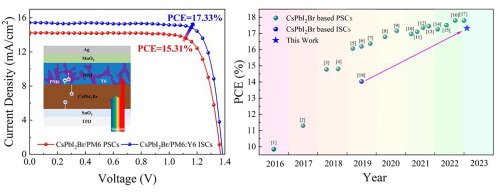
17.3% efficiency CsPbI2Br solar cells by integrating a Near-infrared absorbed organic Bulk-heterojunction layer
Qiang Guo, Zheng Dai, Chuanqi Dong, Yuanjia Ding, Naizhong Jiang, Zhibin Wang, Lei Gao, Chen Duan, Qing Guo, Erjun Zhou,
17.3% efficiency CsPbI2Br solar cells by integrating a Near-infrared absorbed organic Bulk-heterojunction layer,
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 461, 2023, 142025, ISSN 1385-8947,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142025.
All-inorganic perovskite solar cells (PSCs) offer excellent thermal stability, but lag in power conversion efficiency compared to hybrid PSCs. Researchers integrated a low bandgap organic active layer (PM6:Y6) to CsPbI2Br PSCs, extending the photo-response range, improving short-circuit current density, and boosting efficiency from 15.31% to 17.33%. This promising strategy demonstrates enhanced performance and deeper understanding of carrier transfer in integrated solar cells.
Transient photovoltage (TPV) and transient photocurrent (TPC) were performed on a Fluxim Paios characterization system with light intensity about 0.278 sun.

Constructing D‑π‑A Type Polymers as Dopant-Free Hole Transport Materials for High-Performance CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells
Zheng Dai, Qiang Guo, Yuanjia Ding, Zhibin Wang, Naizhong Jiang, and Erjun Zhou
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 7, 9784–9791
Publication Date:February 9, 2023
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c23036
Efficient and stable perovskite solar cells (PSCs) rely heavily on hole-transporting materials (HTMs), with dopant-free conjugated polymers gaining interest for their high hole mobility and stability. A recent study explored the relationship between polymer structure and photovoltaic performance by using three D-π-A-type polymers with varying A units.
The energy levels, hole mobility, molecular stacking, and charge transfer were investigated for CsPbI2Br PSCs with these HTMs. The device using PE61 HTM achieved the highest power conversion efficiency at 16.72%, outperforming PBDB-T (15.13%) and J52 (15.52%), and exhibited the best long-term stability.
This demonstrates that quinoxaline is an effective A unit for D-π-A-type polymers, improving PSC photovoltaic performance.
Transient photocurrent (TPC) and transient photovoltage (TPV) were tested by a Fluxim Paios characterization system.
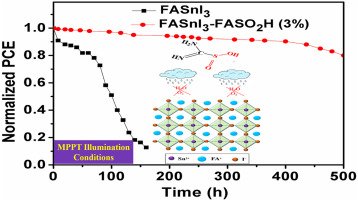
Regulated oxidation and moisture permeation via sulfinic acid based additive enables highly efficient and stable tin-based perovskite solar cells
Muhammad Abdel-Shakour, Kiyoto Matsuishi, Towhid H. Chowdhury, Ashraful Islam,
Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,
Volume 254, 2023, 112241, ISSN 0927-0248,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2023.112241.
Researchers are exploring Sn-based perovskite solar cells as a non-toxic alternative, but challenges remain due to oxidation and moisture permeation. A recent study used a Lewis base additive, formamidinesulfinic acid (FASO2H), to address these issues. Results showed a 32% reduction in Sn2+/Sn4+ oxidation, improved crystallinity, and a 66% decrease in lattice strain. The modified cells achieved a 7.44% power conversion efficiency and demonstrated superior moisture protection and light soaking stability, retaining 90% of initial efficiency after 450 hours.
Dark J-V and EIS for the fabricated PSCs were calculated using Paios.
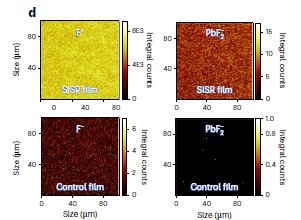
Surface in situ reconstruction of inorganic perovskite films enabling long carrier lifetimes and solar cells with 21% efficiency
Chu, X., Ye, Q., Wang, Z. et al.
Nat Energy (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01220-z
Researchers developed a surface in situ reconstruction (SISR) strategy using CsF treatment to improve all-inorganic perovskite solar cells. The treatment suppresses non-radiative recombination, passivates surface defects, and promotes hole extraction. It results in a longer carrier lifetime and creates a graded heterojunction. As a result, CsPbIxBr3−x solar cells with SISR achieve a 21.02% efficiency, a 1.27 V open-circuit voltage, and an 85.3% fill factor. This work offers an effective approach to enhance inorganic perovskite surfaces for efficient solar cells.
Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), capacitance–voltage (C–V) and photogenerated charge extraction by linearly increasing voltage (photo-CELIV) mobilities data were measured by the all-in-one characterization platform Paios (Fluxim AG) in air conditions without encapsulation.
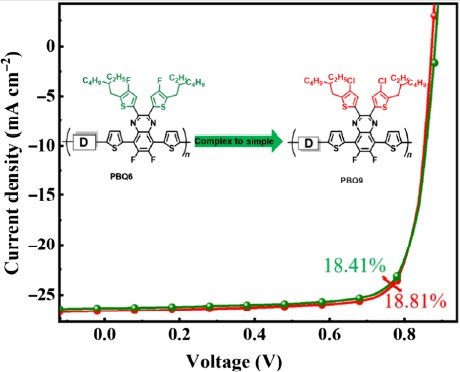
A-Unit with Alkyl-Chlorothiophene Substituents for Polymer Solar Cells
Can Zhu, Ke Hu, Lei Meng, Xiaolei Kong, Wenbin Lai, Shucheng Qin, Beibei Qiu, Jinyuan Zhang, Zhanjun Zhang, Yilei Wu, Xiaojun Li, and Yongfang Li
CCS Chem. Jan 4, 2023,
DOI: 10.31635/ccschem.022.202202491
Researchers have developed a new D-A copolymer donor, PBQ9, which is based on difluoroquinoxaline A-unit with chlorine substitution on its alkyl-thiophene side chains instead of fluorine substitution. Chlorine substitution is less complicated and less costly than fluorine substitution.
The optimized binary polymer solar cell (PSC) using PBQ9 as the polymer donor and m-TEH as the acceptor showed a high power conversion efficiency of 18.81%, with a high fill factor of 80.59%, and the photovoltaic performance was insensitive to different batches of the polymer donor. The results indicate that PBQ9 is a high-performance polymer donor, and chlorine substitution is an effective strategy to improve the photovoltaic performance and reduce the cost of polymer donors.
Photo-CELIV and TPC measurements:were obtained by the all-in-one characterization platform, Paios.

Evaporated Self-Assembled Monolayer Hole Transport Layers: Lossless Interfaces in p-i-n Perovskite Solar Cells
Farag, A., Feeney, T., Hossain, I. M., Schackmar, F., Fassl, P., Küster, K., Bäuerle, R., Ruiz-Preciado, M. A., Hentschel, M., Ritzer, D. B., Diercks, A., Li, Y., Nejand, B. A., Laufer, F., Singh, R., Starke, U., Paetzold, U. W.,
Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 2203982.
https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202203982
This openaccess research article discusses the use of vacuum-based evaporation to deposit self-assembled monolayers (SAM-HTLs) based on carbazole functional groups with phosphonic acid anchoring groups in perovskite solar cells (PSCs). SAM-HTLs have previously been deposited exclusively via solution-based methods. The authors found that vacuum deposition preserves or even slightly improves the near lossless interfacial properties and is also found to improve perovskite wetting and fabrication yield on previously non-ideal materials. This research provides a new method for depositing SAM-HTLs and improving the versatility of these materials without sacrificing their beneficial properties.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): EIS for the full device stack was conducted using Paios. The sweep frequency was from 1 Hz to 1 MHz with 70 mV amplitude and offset voltage equivalent to the device's VOC.
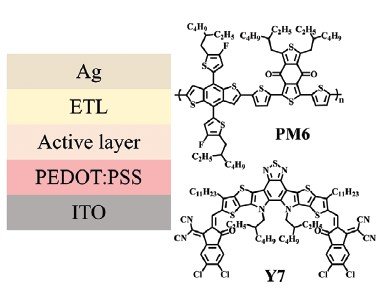
An n-n Heterojunction Configuration for Efficient Electron Transport in Organic Photovoltaic Devices
Li, Y., Wu, X., Zuo, G., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Ma, Y., Li, B., Zhu, X.-H., Wu, H., Qing, J., Hou, L., Cai, W.,
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 2209728. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202209728
This work presents a new electron transport layer (ETL) configuration for organic photovoltaics (OPVs) that comprises a solution-processed n-n organic heterojunction. The n-n heterojunction is constructed by stacking a narrowband n-type conjugated polymer layer and a wide-band n-type conjugated molecule layer to enhance electron transport and hole blocking, and boost power conversion efficiency (PCE) in OPV.
The new ETL configuration leads to substantial improvements in performance in three OPVs with different active layers due to the combination of selective carrier transport properties and reduced recombination, as well as the good film-forming quality of the new ETL configuration.
Device Characterization: The transient photovoltage (TPV) and photocurrent (TPC) measurements were characterized with PAIOS system (Fluxim) under open-circuit condition and a short-circuit condition, respectively.
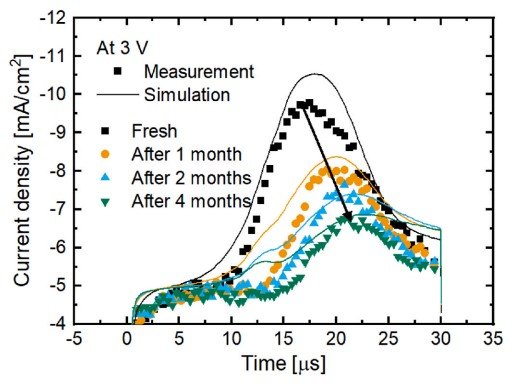
Pinpointing the origin of the increased driving voltage during prolonged operation in a phosphorescent OLED based on an exciplex host
Markus Regnat, Chang-Ki Moon, Sandra Jenatsch, Beat Ruhstaller, Kurt P. Pernstich,
Organic Electronics, Volume 108, 2022, 106570, ISSN 1566-1199,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2022.106570.
Highlights
• Increased driving voltage after prolonged operation.
• Radiant flux remained constant, so an electrical model is sufficient.
• Using multiple measurement methods, determine reliable model parameters.
• Sensitivity analysis reveals the origin of the increased driving voltage.
• Hole traps in TAPC are the main cause of the increased driving voltage.
Fluxim’s all-in-one measurement system, Paios, equipped with a temperature module and a photomultiplier from Hamamatsu (H11526 Series), was used to measure OLED characteristics.
Fluxim's Characterization Suite software (version 4.3) was used to analyze the obtained data, which included the Setfos-Paios-Integration feature for performing model parameter optimizations for fitting the measured data.
An embedded interfacial network stabilizes inorganic CsPbI3 perovskite thin films
Steele, J.A., Braeckevelt, T., Prakasam, V. et al.
Nat Commun 13, 7513 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35255-9
The black perovskite phase of CsPbI3 is promising for optoelectronic applications; however, it is unstable under ambient conditions, transforming within minutes into an optically inactive yellow phase, a fact that has so far prevented its widespread adoption.
In this paper the research team present an effective strategy for embedding an interfacial microstructure (a PbI2 microgrid) into stable CsPbI3 perovskite thin films and devices, using a coarse photolithographic approach. The microgrid is shown to dramatically increase the long-term stability of black CsPbI3 thin films (beyond 2.5 years in a dry environment) by increasing the phase transition energy barrier (Eb) and limiting the spread of potential yellow phase formation to a single, isolated domain of the grid.
Using stabilized photodetectors, integration of a microgrid into normally unstable planar CsPbI3 perovskite devices is shown to be a simple and effective strategy toward stable ambient operation.
Paios was used to measure the rise and decay time and the capacitance of the devices. The pulsed J-V characteristics were measured from 2 V to −1 V with 50 ms, 1 ms, and 25 ms as the pulse length, rise time, and measurement time, respectively.

Traps for Electrons and Holes Limit the Efficiency and Durability of Polymer Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells
M. Diethelm, A. Devižis, W.-H. Hu, T. Zhang, R. Furrer, C. Vael, S. Jenatsch, F. Nüesch, R. Hany
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203643. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202203643
This research investigates the impact of electron and hole traps on the performance and lifespan of polymer light-emitting electrochemical cells (PLECs). The study aims to identify and analyze the role of these traps in PLECs, drawing parallels with their known impact on polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs).
The researchers fabricated PLECs using a super yellow (SY) polymer as the emitting material and employed various experimental techniques, including electrical driving and breaks, light irradiation, and long-term absorption and capacitance measurements. Optical and electrical simulations using Setfos provided further insights into device behavior.
The findings reveal that electron traps in PLECs share similar characteristics with those in PLEDs, suggesting a common origin in the semiconducting polymer. Notably, the study identifies two types of hole traps in PLECs: one type present in the intrinsic region, mirroring PLED behavior, and another type forming at the interface of the intrinsic and p-doped regions, specific to the PLEC architecture.
This research highlights the significant role of charge traps in limiting PLEC performance and longevity. The findings emphasize the need for strategies beyond conventional approaches to enhance PLEC stability, urging a focus on addressing the fundamental limitations posed by charge traps within the light-emitting polymer itself.
How Setfos Was Used
Setfos was used to perform optical and electrical simulations of the PLEC devices to better understand their properties, such as luminance versus emitter position.
How Paios Was Used
Paios was used to perform several different types of measurements on the PLEC devices:
Impedance measurements: Specifically, impedance measurements at 0 V with an alternating 70 mV signal were taken to determine the capacitance transients of the devices.
Current and light intensity transient measurements: The Paios measurement system was also used to measure how the current and light intensity changed over time. The light intensity was measured by using a photodiode to measure the photovoltage, and the relationship between the measured photovoltage and the corresponding radiance/luminance is explained in a different source.
How Phelos Was Used
Phelos was used to take angular-dependent electroluminescence (EL) measurements of the PLEC devices.

A Thiourea Competitive Crystallization Strategy for FA-Based Perovskite Solar Cells
Sun, Q., Tuo, B., Ren, Z., Xue, T., Zhang, Y., Ma, J., Li, P., Song, Y.
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 2208885.
doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202208885
Yanlin Song and colleagues at the Chinese Academy of Sciences embedded TU as a dopant in PbI2 and they used it as interface treatment at the SnO2/perovskite interface. Devices with either of the two treatments presented larger grains, and lower defect concentration. The treatment released tensile stress in the #perovskite by reducing the interface lattice mismatch at the SnO2/perovskite heterojunction. The champion solar cell reached a PCE of 24.4% and retained 80% of the initial efficiency after 120 hours of stressing at 60°C in N2.
Transient photocurrent (TPC), transient photovoltage (TPV), and space-charge limited current (SCLC) were performed with Paios from FLUXiM AG. These experiments confirmed the improvement in charge carrier transport and reduction in recombination thanks to the reduced defect concentration.
Importance of structural hinderance in performance–stability equilibrium of organic photovoltaics
Fan, B., Gao, W., Wu, X. et al.
Nature Communications 13, 5946 (2022).
doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33754-3
Power conversion efficiency and long-term stability are two critical metrics for evaluating the commercial potential of organic photovoltaics.
Although the field has witnessed a rapid progress of efficiency towards 19%, the intrinsic trade-off between efficiency and stability is still a challenging issue for bulk-heterojunction cells due to the very delicate crystallization dynamics of organic species. Herein, the research team from the City University of Hon Kong developed a class of non-fullerene acceptors with varied side groups as an alternative to aliphatic chains.
Delay-time charge extraction by linearly increasing voltage (CELIV) was measured on the all-in-one platform of Paios (FluximAG). A light pulse with duration of 50 μs generated from an 810 nm LED lamp (light intensity 100%) was applied prior to a voltage ramp of 1 V μs–1.
The delay time between light pulse and voltage ramp was varied from 0.2 to 10 μs. During the delay time, the open circuit was kept by applying the transient photovoltage signal to ensure no current is flowing.
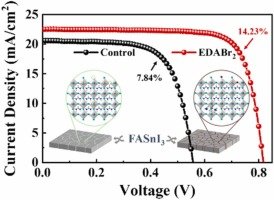
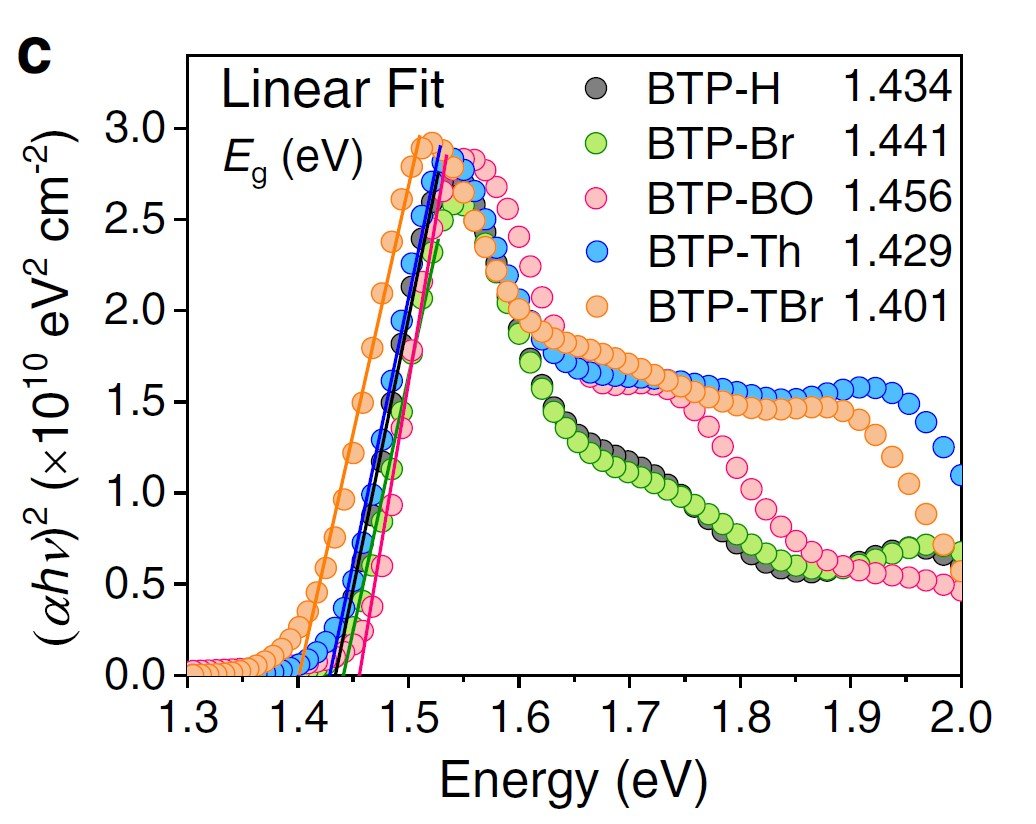
Dual-site passivation of tin-related defects enabling efficient lead-free tin perovskite solar cells
Yiting Jiang, Zhengli Lu, Shengli Zou, Huagui Lai, Zhihao Zhang, Jincheng Luo, Yuanfang Huang, Rui He, Jialun Jin, Zongjin Yi, Yi Luo, Wenwu Wang, Changlei Wang, Xia Hao, Cong Chen, Xin Wang, Ye Wang, Shengqiang Ren, Tingting Shi, Fan Fu, Dewei Zhao,
Nano Energy, Volume 103, Part A, 2022, 107818, ISSN 2211-2855,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107818.
Ethylenediammonium halide salts (i.e., EDAI2 and EDABr2) are good candidates to passivate Sn oxidation and deep traps in lead-free Sn-based Perovskite.
The group of Dewei Zhao at the Institute of New Energy and Low-Carbon Technology in Sichuan university recently discovered that EDABr2-modified perovskite devices could achieve 14.23% efficiency and retain 95% of the performance after 110 hours at operating conditions.
By performing transient photocurrent (TPC) and transient photovoltage (TPV) measurements with the Paios tool from Fluxim AG, they observed a TPC lifetime improvement from 1.29 us to 0.74 us and TPV lifetime from 5.9 us to 37.83 us, confirming the improved charge transport and charge recombination lifetimes.
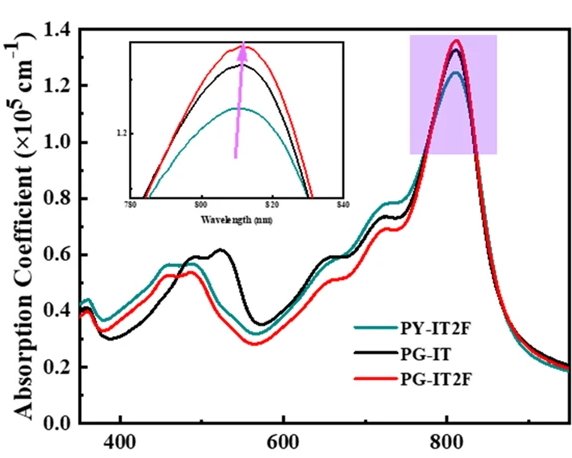
High performance polymerized small molecule acceptor by synergistic optimization on π-bridge linker and side chain
Sun, G., Jiang, X., Li, X. et al.
Nat Commun 13, 5267 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32964-z
Polymeric small molecule acceptors (PSMAs) are narrow bandgap small-molecule acceptors (SMAs) copolymerized with a π-bridge linking unit (linker). A power conversion efficiency of 17.24% was reached recently at the Beijing National Laboratory of Molecular Sciences by testing three PY-IT derivatives. PG-IT2F was the champion polymer with lower recombination and improved charge transport.
And FLUXiM AG tools are supporting their research. With Paios they performed light-dependent transient photovoltage (TPV) measurements and estimated a charge lifetime of 0.769 us on PG-IT2F-based solar cells compared to 0.436 us for the reference PY-IT PVs.
Interfacial Embedding for High-Efficiency and Stable Methylammonium-Free Perovskite Solar Cells with Fluoroarene Hydrazine
Dhruba B. Khadka, Yasuhiro Shirai, Masatoshi Yanagida, Terumasa Tadano, Kenjiro Miyano
Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 2202029
doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202202029
Surface treatment with fluoroarene derivatives increases the efficiency and long-term stability of MA/Br-free #perovskites.
Recently, researchers at the National Institute for Materials Science reached a certified 21% efficiency on a 1cm^2 #perovskite solar cell that does not contain the thermally unstable methylammonium (MA) or Br. This was possible through surface passivation based on fluoroarene derivatives. The passivated device retains 80% of the performance after 300h at 60-65% of humidity and about 90% after 500h at 65°C.
With #Paios from FLUXiM AG they measured lower defect density and slower photovoltage decay by means of capacitance-voltage (CV) and transient photovoltage (TPV), respectively, which confirms defects passivation. Paios is an all-in-one instrument that allows full optoelectrical characterization of solar cells and LEDs.

Heterogeneous Integration of Colloidal Quantum Dot Inks on Silicon Enables Highly Efficient and Stable Infrared Photodetectors
Qiwei Xu, I. Teng Cheong, Hanfa Song, Vien Van, Jonathan G. C. Veinot, and Xihua Wang
ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 8, 2792–2801
doi/pdf/10.1021/acsphotonics.2c00587
Integrating lead sulfide (PbS) colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) with crystalline silicon (c-Si) has been proven to be an effective strategy in extending the sensitivity of Si-based photodetectors into infrared regime. Here, the research team demonstrate the successful integration of PbS CQD inks with Si and construct a highly efficient heterojunction infrared photodiode operating in the range from 800 up to 1500 nm.
Summary points:
∙PbS CQD on Si to increase sensitivity of Si to IR
∙CQD:Si photodetector operating from 800 to 1500 nm
∙Layer of p-type QD enhances built-in electric field
∙EQE of 44% at 1280nm and 2V reverse bias - stable for more than 600 h
∙Photoresponse lower than 4μs without tails indicate low trap density
Lead sulfide (PbS) colloidal quantum dots (CQD) enable Si photodector sensitivity in the near infrared (NIR) in the range from 800 to 1500 nm.
The group of Xihua Wang at the University of Alberta achieved this result by spin-coating PbS CQD to form a CQD:Si heterojunction photodetector. The addition of a p-type CQD buffer layer at the CQD:Si interface enhanced the built-in electric field and improved the charge extraction. With transient photocurrent (TPC) and photovoltage (TPV) they measured a photoresponse lower than 4μs demonstrating low trap density at the CQD:Si interface.
TPC and TPV measurements were possible thanks to the all-in-one characterization platform PAIOS from Fluxim AG.
Colloidal III–V Quantum Dot Photodiodes for Short-Wave Infrared Photodetection
Leemans, J., Pejović, V., Georgitzikis, E., Minjauw, M., Siddik, A. B., Deng, Y.-H., Kuang, Y., Roelkens, G., Detavernier, C., Lieberman, I., Malinowski, P. E., Cheyns, D., Hens, Z.
Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200844.
doi.org/10.1002/advs.202200844
QD-photodetectors are cost-effective, have small pixel pitch, and high spectral tunability, but they generally rely on restricted elements such as Pb and Hg. The team at Ghent University and imec fabricated high-efficiency photodetectors with non-restricted In(As,P) QDs deposited by spin-coating. These devices exhibit the best internal quantum efficiencies at the QD band gap of 46±5% and are sensitive to SWIR light up to 1400 nm.
Paios was used to characterize the photodetectors both in DC and transient modes. Thanks to all co-authors for your trust in our products.

Organic Solar Cell With Efficiency Over 20% and VOC Exceeding 2.1 V Enabled by Tandem With All-Inorganic Perovskite and Thermal Annealing-Free Process
Xiaoyu Gu, Xue Lai, Yuniu Zhang, Teng Wang, Wen Liang Tan, Christopher R. McNeill, Qian Liu, Prashant Sonar, Feng He, Wenhui Li, Chengwei Shan, and Aung Ko Ko Kyaw
Adv. Sci. 2022, 2200445
doi/pdf/10.1002/advs.202200445
∙TA vs TA-free to optimize Voc loss in OSC (CV, EIS
∙20.6% small area, 16.5% large area
∙high Voc. Champion has Voc loss of 0.001V (almost perfect ICL)
∙Eg 1.4 and 1.9
∙700h stability in N2
1mV difference between the Voc of an organic-perovskite tandem solar cell and the sum of the individual sub-cells. Almost perfect charge transport.
The tandem is a combination of an organic PM6:Y6 (1.49eV) and an all-inorganic perovskite (1.92eV). The remarkable result was obtained by the group of Aung Ko Ko Kyaw at the Gunagdong University by optimizing the electron transport of the perovskite subcell and the interconnection layer (ICL) between the subcells.
Investigation of thermal annealing (TA) treatments effect revealed that TA creates a barrier at the ICL (electrode/PFN-Br interface), hence it must be avoided for efficient charge transport between the subcells.
This result was obtained by carrying out capacitance and impedance measurements with the all-in-one platform Paios from Fluxim AG.
A Multifaceted Ferrocene Interlayer for Highly Stable and Efficient Lithium Doped Spiro-OMeTAD-based Perovskite Solar Cells
Thomas Webb, Wei Zhang et al
Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 2200666
Over the last decade spiro-OMeTAD has remained the hole transporting layer (HTL) of choice for producing high efficiency perovskite solar cells (PSCs).
However, PSCs incorporating spiro-OMeTAD suffer significantly from dopant induced instability and non-ideal band alignments. Herein, a new approach is presented for tackling these issues using the functionality of organometallocenes to bind to Li+ dopant ions, rendering them immobile and reducing their impact on the degradation of PSCs.
The electrical impedance spectra were recorded on the all-in-one Paios characterization platform
Semitransparent Organic Solar Cells with Efficiency Surpassing 15%
Jianhua Jing, Sheng Dong, Kai Zhang,* Zhisheng Zhou, Qifan Xue, Yu Song, Zurong Du, Minrun Ren, and Fei Huang
Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 2200453
Semitransparent organic solar cells (ST-OSCs) have promising prospects for building or vehicle integrated solar energy harvesting with energy generation and see-through function. How to achieve both an adequate average visible transmittance (AVT) and high-power conversion efficiency (PCE) is always the key issue.
Herein, a simple but effective strategy for constructing high performance ST-OSCs by introducing a small molecule [2-(9-H-Carbazol9-yl) ethyl] phosphonic acid (2PACz) into a low-donor content active layer is reported.
The TPV technique using Paios was based on monitoring the photovoltage decay upon a small optical perturbation during different constant bias light-intensity. As were dark C–V measurements.
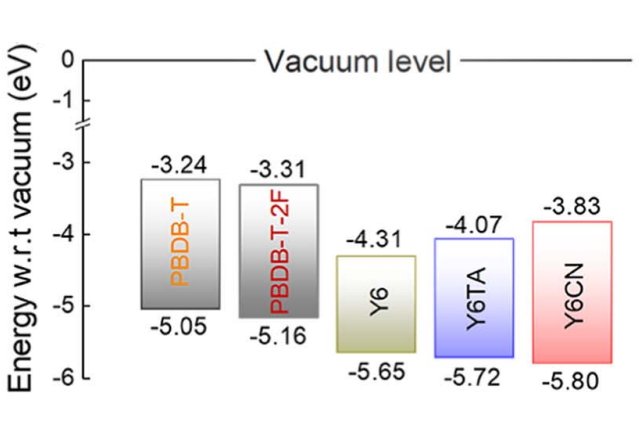
Charge transport and recombination in wide-bandgap Y6 derivatives-based organic solar cells
Yuliar Firdaus, Thomas D. Anthopoulos, et al
2022 Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13 025001
The power conversion efficiency of nonfullerene-based organic solar cells (OSCs) has recently exceeded 18%, thanks to the constant effort to identify the key properties governing the OSCs performance and development of better photovoltaic materials.
With its superior properties, low-bandgap Y6 and its derivatives have emerged as one of the most popular nonfullerene acceptors (NFAs) for OSCs. In this work, the researchers compare two wide-bandgap Y6 derivatives with different end-groups, and their distinct device performance is correlated with their charge transport and recombination properties.
Light-intensity dependence measurements (J-V, TPV, CE, TPC) were performed with Paios.

Charge Transport in Perylene Based Electron Transporting Layer for Perovskite Solar Cells
Kanyaporn Thubthong, Psisit Kumnorkaew, Anusit Kaewprajak, Khathawut Lohawet, Wiyada Saennawa, Vinich Promarak, Yingyot Infahsaeng,
Thin Solid Films, Volume 741, 2022, 139012,
doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2021.139012
In this study, the researchers introduce a bis (perylene diimide) derivative as a buffer layer of the electron transporting layer by the rapid convective deposition technique. The maximum power conversion efficiency of 13.38% with less hysteresis is achieved from the device with perylene diimide as the electron transporting layer. Further, we found that the performance of the perylene-based device is enhanced due to the lower transporting resistance and the increasing electron mobilities. These results suggest that the perylene diimide derivatives can play a crucial influence in the charge transporting enhancement of perovskite solar cells.
Electron Trap Dynamics in Polymer Light-Emitting Diodes
Matthias Diethelm, Michael Bauer, Wei-Hsu Hu, Camilla Vael, Sandra Jenatsch
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 2106185
In this paper the researchers investigate electron trap dynamics in SY PLEDs and discover a recovery feature of the traps during stress interruption. Formation of this trap states takes several minutes. Same behaviour was found for P3HT, MEH-PPV.
The optical and electrical characterization tool Paios was used to stress the PLED and investigate trap dynamics with/without light bias. Additionally TEL experiments show an overshoot if the break time between stressing is extended. Transient Setfos simulations for fast trap dynamics and steady-state voltage depending on Nt.
Photodetectors Based on Lead Sulfide Quantum Dot and Organic Absorbers for Multispectral Sensing in the Visible to Short-Wave Infrared Range
Vladimir Pejović, Epimitheas Georgitzikis, Itai Lieberman, Paweł E. Malinowski, Paul Heremans, David Cheyns
Adv Funct. Mat., (2022)
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202201424
Image sensors based on colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) are expected to deliver affordable infrared image sensors to wider application scope. Here, a dual-band photodetector based on PbS CQDs is presented. By engineering the surface of CQDs, two oppositely facing pn junctions are fabricated in series, which enable sensing in two spectral channels. The presented photodetectors exhibit low dark current below 500 nA cm−2 at 1 V bias, a fast response measured in microseconds, as well as high external quantum efficiency, reaching 70% in NIR and 30% in SWIR.

Properties and Applications of Copper(I) Thiocyanate Hole-Transport Interlayers Processed from Different Solvents
Bingjun Wang, Sungho Nam, Saurav Limbu, Ji-Seon Kim, Moritz Riede, and Donal D. C. Bradley
Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 2101253
Copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN) is an effective interlayer material for hole injection and transport in organic electronic devices but its solution processing has conventionally utilized undesirable di-n-alkyl sulfide solvents such as diethyl- (DES) and dipropyl-sulfide (DPS). Herein, this paper reports on the use of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) as alternative solvents for CuSCN interlayers and performs a detailed comparison of the resulting properties relative to films processed from DES and DPS and two other recent alternatives, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and ammonium hydroxide.
MIS-CELIV experiments were performed using the Fluxim PAIOS measurement platform with Characterization Suite 4.2 software.
Homogeneous Grain Boundary Passivation in Wide-Bandgap Perovskite Films Enables Fabrication of Monolithic Perovskite/Organic Tandem Solar Cells with over 21% Efficiency.
Yue-Min Xie, Yong Cao et al.
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 2112126.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202112126
Monolithic perovskite/organic tandem solar cells have attracted increasing attention due to their potential of being highly efficient while compatible with facile solution fabrication processes. This work has carefully optimized mixed halide wide-bandgap perovskite (MWP) films by introducing a small amount of formamidinium (FA+) cations into the basic composition of MA1.06PbI2Br(SCN)0.12, which provides an effective means to modulate the crystallization properties and phase stability of the films. At optimized conditions, the MA0.96FA0.1PbI2Br(SCN)0.12 forms high-quality films with grain boundaries homogeneously passivated by PbI2, leading to a reduction in defect states and an enhancement in phase stability, enabling the fabrication of perovskite solar cells with a power conversion efficiency(PCE) of 17.4%. By further integrating the MWP front cell with an organic BHJ (PM6:CH1007) rare cell composed of a non-fullerene acceptor with absorption extended to 950 nm, a tandem cell with PCE over 21% is achieved.
PAIOS was used to analyze these solar cells with Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
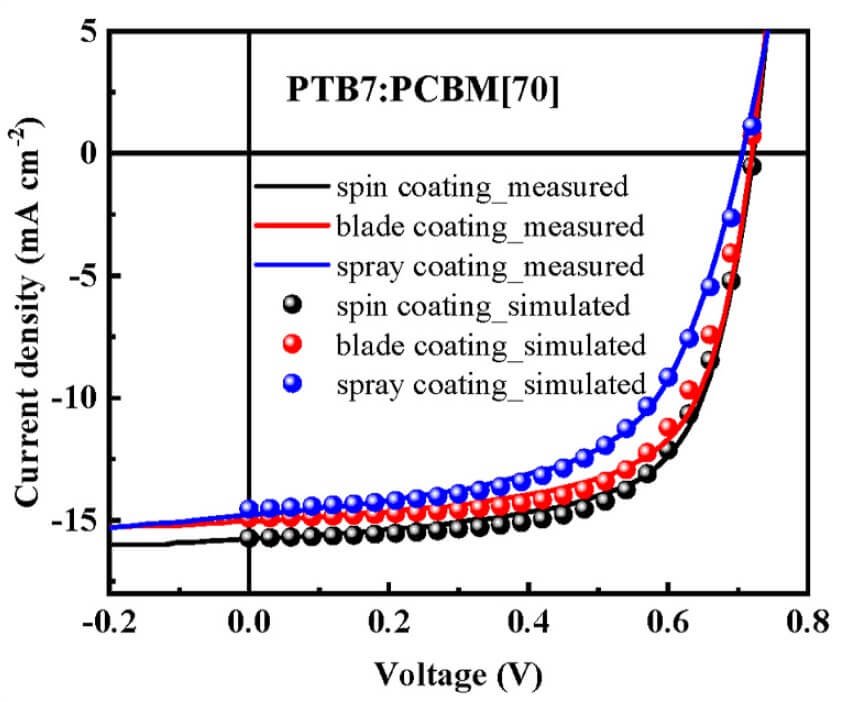
Impact of charge generation and extraction on photovoltaic performances of spin- and blade-as well as spray-coated organic solar cells
Le Wang, Feng Yu, Hong Zhao, Yufei Wang, Tianfu Gu, Wenyan Su, Quanbin Liang, Zhenfang Tang, Hongbin Wu, Lintao Hou
Organic Electronics, Volume 101, 2022
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2021.106423
In this paper the researchers compare the performance of fullerene and non-fullerene based solar cells fabricated with spin, blade or spray coating. They find that spin-coated device have higher performance and analyse it with drift-diffusion simulations of IV curves.
Paios was used to calculate Voc vs. L to substantiate more SRH recombination in spray coated device. They also used TPV and TPC to further substantiate their findings related to different aggregation.

Vacuum deposited WO3/Al/Al:Ag anode for efficient red organic light-emitting diodes
Kevin Sutanto, Nurul Ridho Al Amin, Chih-Hsin Chen, Dian Luo, Chien-Hsin Chen, Sajal Biring, Chih-Chien Lee, Shun-Wei Liu
Organic Electronics, Volume 103, 2022, 106454, ISSN 1566-1199,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2022.106454.
Here the researchers report on a WO3/Al/Al:Ag anode which is demonstrated in a red OLED with superior performance compared to the ITO reference device. Better performance is due to narrower emission spectrum, improved outcoupling, lower turn-on voltage/better charge injection.
Paios was also used to perform Impedance Spectroscopy at different voltages to check injection/accumulation of charges, performed C-V to analyse onset and show Transient Electroluminescence.
Silicon Surface Passivation for Silicon-Colloidal Quantum Dot Heterojunction Photodetectors.
Xu, Qiwei; Cheong, I Teng; Meng, Lingju; Veinot, Jonathan G. C.; Wang, Xihua
ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11, 18429–18436.
doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c08002
In this paper the researchers test different Si passivation tricks to optimize PbS quantum dot detectors. The two-step passivation device shows an EQE of 31% at 1280 nm and -4V.
Paios was used to perform TPV and TPC measurements to confirm longer lifetime and faster extraction, respectively, using the two-step process. This is explained by trap passivation.
Spacer Engineering of Diammonium-Based 2D Perovskites toward Efficient and Stable 2D/3D Heterostructure Perovskite Solar Cells
Tianqi Niu, Yue-Min Xie, Qifan Xue, Sangni Xun, Qin Yao, Fuchao Zhen, Wenbo Yan, Hong Li, Jean-Luc Brédas, Hin-Lap Yip, Yong Cao
Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 2102973.
doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202102973
Here researchers developed a stable and efficient Perovskite solar cell by combining the efficiency of 3D perovskites and the high stability of 2D perovskites.
They compared PSCs with 2D perovskites based on diammonium ligands with different concentrations and sizes. The 2,2-(ethylenedioxy)bis(ethylammonium) (EDBE) cations guarantee a homogenous growth and good coverage of the 2D perovskite layer on top of the 3D absorber. The 2D layer improves photo-, thermal- and humidity stability while increasing the efficiency by 2.5% compared to the control device. The power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the best solar cell was 22.6%.
The boost in performance is the result of decreased charge recombination and improved charge extraction as confirmed by TPC and TPV measurements carried with Paios.

Decoupling the effects of defects on efficiency and stability through phosphonates in stable halide perovskite solar cells
Haibing Xie, Zaiwei Wang, Zehua Chen, ..., Michael Gratzel,
Anders Hagfeldt, Monica Lira-Cantu et al.
Joule Volume 5, Issue 5, 19 May 2021, Pages 1246-1266
doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2021.04.003
"Add H3pp to perovskite to improve performance while maintaining high efficiency (21% maintained after 1000 h @ MPP).
Perform various characterization and simulation techniques to demonstrate that the addition of H3pp leads to a passivation of the shallow defects, which are not affecting the performance but the device stability."
Voc vs L was performed using Paios to demonstrate negligible difference in n_id -> no difference in SRH.
C-f was carried out to demonstrate an effective reduction in ion migration and charge accumulation in the better device.
TPC and OCVD confirm negligible changes in the charge transport mechanism.

Fluorinated Oligomer Wrapped Perovskite Crystals for Inverted MAPbI 3 Solar Cells with 21% Efficiency and Enhanced Stability
Xie, Lisha; Xie, Junni; Wang, Shurong; Chen, Bin; Yang, Chenguang; Wang, Zhen; et al.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22, 26093–26101
doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c06216
In this paper the researchers report on a oligomer treatment of MAPI films which efficiently passivate defects by coordination with Pb ions. With additional improvements in crystallization and charge transport properties, the resulting cell had a PCE of 21.23% and showed better stability.
Paios was used to determine shorter TPC decay time and longer TPV lifetime was used to confirm the improved charge extraction properties.

Tuning of the Interconnecting Layer for Monolithic Perovskite/ Organic Tandem Solar Cells with Record Efficiency Exceeding 21%
Pang Wang, Wei Li, Oskar J. Sandberg, Chuanhang Guo, Rui Sun, Hui Wang, Donghui Li, Huijun Zhang, Shili Cheng, Dan Liu, Jie Min, Ardalan Armin, and Tao Wang
Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 18, 7845–7854
Publication Date:September 10, 2021
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02897
In this paper the researchers utilize the wide-bandgap CsPbI2Br semiconductor and narrow-bandgap PM6:Y6-BO blend to fabricate perovskite/organic tandem solar cells with an efficiency of 21.1% and a very small tandem open-circuit voltage loss of 0.06 V.
The photon absorption rate distribution of polyTPD and PBDB-T-Si based TSCs were simulated using the transfer-matrix model via SETFOS (version number: SETFOS 5.1)

Effect of anode interfacial modification on the performance of laminated flexible ITO-free organic solar cells
Lin Z, Guan W, Cai W, et al.
Energy Sci Eng. 2021;9:502–508.
Lamination technique is one of the most promising and effective approaches to produce flexible organic solar cells (OSCs). In this study, flexible ITO-free OSCs were successfully fabricated by lamination technique under the optimized temperature and pressure. This work illustrates that anode interface engineering has a significant effect on the improvement of performance of roll-to-roll laminated and self-encapsulated OSCs.
The light intensity dependence and spectroscopy (IS) as well as photo-induced charge extraction by linearly increasing volt-age (photo-CELIV) measurements were performed using an all-in-one electrical and optical characterization platform of Paios.

Helical Copper Redox Mediator with Low Electron Recombination for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Zijian Deng, Xichuan Yang, Kaiyuan Yang, Li Zhang, Haoxin Wang, Xiuna Wang, and Licheng Sun
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2021 9 (15), 5252-5259
DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08195
Redox mediators play a major role in determining the photocurrent and photovoltage in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). In this study, two helical copper(I) complexes are synthesized and applied to TBP-free solar cells.
As part of this study the researchers used Paios to perform Intensity-modulated photovoltage spectroscopy (IMVS)

High-efficiency lead-free wide band gap perovskite solar cells via guanidinium bromide incorporation
Mengmeng Chen, Muhammad Akmal Kamarudin, Ajay K. Baranwal, Gaurav Kapil, Teresa S. Ripolles, Kohei Nishimura, Daisuke Hirotani, Shahrir Razey Sahamir, Zheng Zhang, Chao Ding, Yoshitaka Sanehira, Juan Bisquert, Qing Shen, and Shuzi Hayase
ACS Applied Energy Materials 2021 4 (6), 5615-5624
In this paper the researchers explore the fabrication of the wide band gap (1.61 eV) ASnI2Br perovskite solar cells through the optimization of formamidinium and guanidinium content to improve the efficiency from 1.68 to 7.00%. This work provides proof that tin-halide perovskite solar cells have the potential in the fabrication of lead-free all-perovskite tandem solar cells.
The researchers used Paios to perform, under light, intensity-modulated photocurrent spectroscopy (IMPS) and intensity-modulated photovoltage spectroscopy (IMVS).

Eco-friendly antisolvent enabled inverted MAPbI3 perovskite solar cells with fill factors over 84%
Yuying Cui, Shurong Wang, Chengbo Li, Aili Wang, Jing Ren, Chenguang Yang, Bin Chen, Zhen Wang and Feng Hao
Green Chem., 2021,23, 3633-3641
A green co-antisolvent of propyl acetate is induced to adjust the degree of supersaturation in diethyl ether, enabling pinhole-free, smooth, and uniform perovskite thin films. A high power conversion efficiency up to 20.61% was achieved in a p–i–n inverted MAPbI3 PSC with an impressive fill factor (FF) over 84%.

Unveiling Roles of Tin Fluoride Additives in High‐Efficiency Low‐Bandgap Mixed Tin‐Lead Perovskite Solar Cells
Qiyu Chen, Jincheng Luo, Rui He, Huagui Lai, Shengqiang Ren, Yiting Jiang, Zhenxi Wan, Wenwu Wang, Xia Hao, Ye Wang, Jingquan Zhang, Iordania Constantinou, Changlei Wang, Lili Wu, Fan Fu, Dewei Zhao
Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 2101045.
doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202101045
In the paper, the researchers analyze the effect of SnF2 additives on the performance of lead-tin perovskite solar cells. The Paios dark IV measurement was used to detect saturation current and attribute this to the defect density.

Making Room for Growing Oriented FASnI 3 with Large Grains via Cold Precursor Solution
Danyu Cui, Xiao Liu, Tianhao Wu, Xuesong Lin, Xinhui Luo, Yongzhen Wu, Hiroshi Segawa, Xudong Yang, Yiqiang Zhang, Yanbo Wang, Liyuan Han
Adv. Fun. Mat. Volume31, Issue25, June 16, 2021, 2100931
doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202100931
Description:
In this paper, the researchers fabricated tin-based perovskite solar cells with improved performance thanks to a cooled (0°) precursor solution. The latter leads to larger grain sizes which enhance the charge carrier lifetime (-> enhanced Voc) and reduces the oxygen penetration (-> longer lifetime) and subsequent reaction in the film. Paios was used to perform TPV and TPC experiments in order to demonstrate the longer charge carrier lifetime and the enhanced charge extraction properties of the 0° -device, respectively.

Perovskite Light-Emitting Devices with Doped Hole Transporting Layer
Zhiwei Peng, Yuhan Gao, Guohua Xie
Molecules 2021, 26(6), 1670
doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061670
Description:
In this paper, the researchers investigated the effect of different dopants for the HTL (PTAA) in perovskite QD LEDs. Doping generally improved the peak efficiency compared to the undoped PTAA device. Paios was used to perform TEL and impedance spectroscopy to support the improved charge transport behavior upon electrical doping.

Suppression of Nonradiative Recombination by Vacuum‐Assisted Process for Efficient Lead‐Free Tin Perovskite Solar Cells
Zhenxi Wan, Shengqiang Ren, Huagui Lai, Yiting Jiang, Xiaojun Wu, Jincheng Luo, Yunfan Wang, Rui He, Qiyu Chen, Xia Hao, Ye Wang, Lili Wu, Iordania Constantinou, Wen-Hua Zhang, Jingquan Zhang, Dewei Zhao
Adv. Mat. Int. Volume8, Issue9 May 7, 2021, 2100135
doi.org/10.1002/admi.202100135
Description:
In this paper, the researchers used a vacuum treatment to improve the performance (Voc and Jsc) of FA0.75MA0.25SnI3 perovskite solar cells.
Paios was used to perform dark IV measurements to support interface trap reduction via decreased J0.

Electric‐Induced Degradation of Cathode Interface Layer in PM7: IT‐4F Polymer Solar Cells
T. Dai, X. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Zhou, Y. Zhu, J. Zhou, D. Xu T. Lin
Solar RRL (5 March 2021);
In this paper, the researchers analyze the effect of the PFN-Br interface layer on the performance and degradation of an OPV. The degradation (electric load) was showing a reduced FF and Jsc which they attributed to the contact modification, as it was absent for the devices without PFN-Br. The researchers used the characterization tool Paios. They performed multiple measurements to support the charge collection/extraction problem due to PFN-Br interface during degradation.

Influence of the organic hole transport layer on the dynamics of quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes
Jörn Langenickel; Alexander Weiß; Jörg Martin; Thomas Otto; Harald Kuhn
SPIE 11706, Light-Emitting Devices, Materials, and Applications XXV, 117061R (5 March 2021);
In this paper, the researchers analyze the influence of organic HTL on the QLED dynamics and mobilities in HTL and correlate this with the dynamics of the QLED (-> determined by Modulated Electroluminescence Spectroscopy (MELS)). The researchers used the characterization tool Paios. In particular, the phase shift from MELS was used as a figure of merit for the QLED dynamics.

Efficient wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells enabled by doping a bromine-rich molecule
Rui He, Dewei Zhao et al.
nanoph-2020-0634 2021,
In this paper, the researchers work on wide bandgap perovskite and achieve an efficiency of 17.12% for their inverted TBB-doped PSC with an enhanced Voc of 1.19 V. The improvement is due to (1) better alignment of the conduction band with C60 and (2) larger grain sizes leading to reduced bulk recombination." The researchers used the characterization tool Paios. TPV (TPC) shows increased (decreased) lifetime (charge extraction time) for 0.3% TBB-doped perovskite solar cell confirming the TrPL lifetimes (UPS energy alignment) data also in the device. IS fitting was interpreted as higher recombination resistance.

Potassium Thiocyanate‐Assisted Enhancement of Slot‐Die‐Coated Perovskite Films for High‐Performance Solar Cells
Fuzong Xu, Stefaan De Wolf, et al.
Small Sci. 2021, 2000044
In this paper, the researchers fabricated MAPI perovskites using slot-die coating with KSCN additive, and a modified solvent mixture. These modifications lead to higher performance (avg PCE 20.14%, all key figures improved), lower hysteresis, and a longer device lifetime. The researchers used the characterization tool Paios to increase TPV lifetime, larger recombination resistance from IS and shorter TPC decay times for KSCN modified cells to support better charge transport properties and lower defect densities.

Chain Conformation Control of Fluorene-Benzothiadiazole Copolymer Light-Emitting Diode Efficiency and Lifetime
Bingjun Wang, Hao Ye, Moritz Riede, and Donal D. C. Bradley
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces Article ASAP (Jan, 2021)
The aim of this research is to fabricate Perovskite LEDs with beta-phase-induced ordered EML. The 5% ordered film shows improved efficiency and lifetime compared to the 0% beta-phase Perovskite LED. Paios was used to balance electron-hole mobilities for beta-phase samples, measured by MIS-CELIV and differential susceptance, which is argued to lead to a better charge balance factor and thus a higher EQE.


































































































