Introducing back-surface field for efficient inverted CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells
hunyan Lu, Xiaodong Li, Haobo Yuan, Wenxiao Zhang, Xuemin Guo, Acan Liu, Hui Yang, Wen Li, Zhengbo Cui, YuYang Hu, Junfeng Fang,
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 480, 2024, 147267, ISSN 1385-8947,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.147267
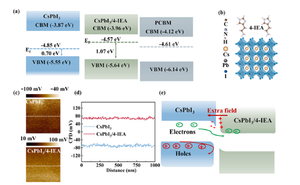
The paper introduces a back-surface field in inverted CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells using 4-Imidazoleethylamine (4-IEA) treatment to improve efficiency and stability. The treatment upshifts the Fermi level at the CsPbI3 surface, creating an extra back-surface field that aligns with the built-in potential of the solar cells. This alignment reduces energy loss and facilitates electron extraction at the CsPbI3/electron transporting layer interface. Additionally, 4-IEA passivates interfacial defects due to its Lewis base-acid interaction with CsPbI3. The result is a power conversion efficiency of 20.22% and good operational stability, retaining over 70% efficiency after 200 hours at 65℃.
How Paios was used
Paios was employed for transient photocurrent decay (TPC) and transient photovoltage (TPV) decay measurements. These measurements were crucial in understanding the dynamic charge transport process in the solar cells. The TPC and TPV results demonstrated a significant reduction in non-radiative recombination and improved charge transport efficiency in the cells treated with 4-IEA, contributing to the overall improved performance of the solar cells.