Manipulation of the Structure and Optoelectronic Properties through Bromine Inclusion in a Layered Lead Bromide Perovskite
Lin-jie Yang, Wenye Xuan, David Webster, Lethy Krishnan Jagadamma, Teng Li, David N. Miller, David B. Cordes, Alexandra M. Z. Slawin, Graham A. Turnbull, Ifor D. W. Samuel, Hsin-Yi Tiffany Chen, Philip Lightfoot, Matthew S. Dyer, and Julia L. Payne
Chemistry of Materials 2023 35 (10), 3801-3814
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c03125
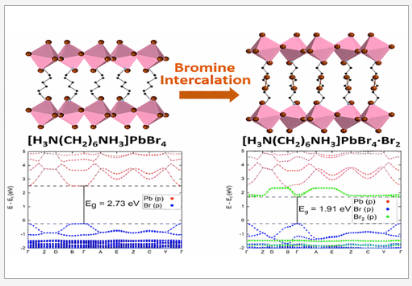
This study demonstrates the tunability of organic-inorganic metal halides through anion substitution, incorporating bromine into [H3N(CH2)6NH3]PbBr4 to create [H3N(CH2)6NH3]PbBr4·Br2. This inclusion of molecular bromine leads to a reduced band gap, structural phase transition, and improved carrier mobility. The key to this manipulation is the formation of halogen bonds between Br2 and Br in the [PbBr4]∞ layers. This work opens possibilities for tuning electronic properties in layered organic-inorganic perovskites and represents the first example of molecular bromine inclusion in such a material.
How Paios was used
The current−voltage measurements were carried out using the all-in-one characterization platform Paios, Fluxim AG, Switzerland. The voltage scan range used was 0−9 V.