Colloidal III–V Quantum Dot Photodiodes for Short-Wave Infrared Photodetection (Copy)
Leemans, J., Pejović, V., Georgitzikis, E., Minjauw, M., Siddik, A. B., Deng, Y.-H., Kuang, Y., Roelkens, G., Detavernier, C., Lieberman, I., Malinowski, P. E., Cheyns, D., Hens, Z.
Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200844.
doi.org/10.1002/advs.202200844
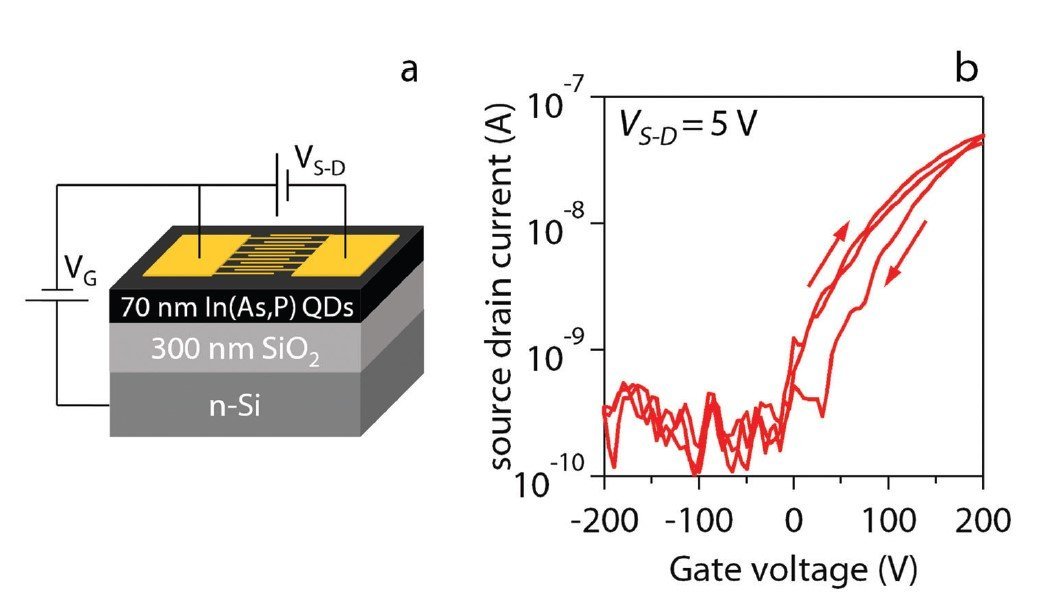
QD-photodetectors are cost-effective, have small pixel pitch, and high spectral tunability, but they generally rely on restricted elements such as Pb and Hg. The team at Ghent University and imec fabricated high-efficiency photodetectors with non-restricted In(As,P) QDs deposited by spin-coating. These devices exhibit the best internal quantum efficiencies at the QD band gap of 46±5% and are sensitive to SWIR light up to 1400 nm.
Paios was used to characterize the photodetectors both in DC and transient modes. Thanks to all co-authors for your trust in our products.