Properties and Applications of Copper(I) Thiocyanate Hole-Transport Interlayers Processed from Different Solvents
Bingjun Wang, Sungho Nam, Saurav Limbu, Ji-Seon Kim, Moritz Riede, and Donal D. C. Bradley
Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 2101253
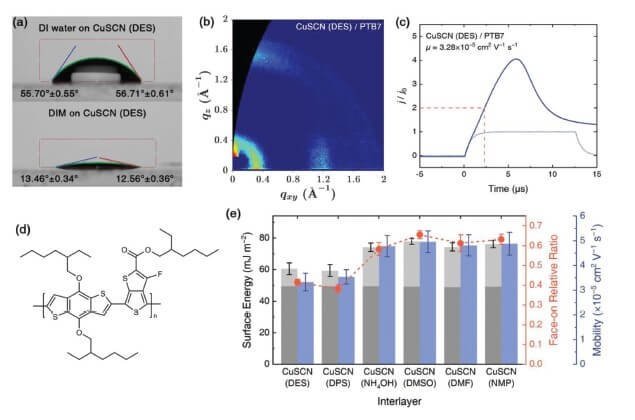
Copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN) is an effective interlayer material for hole injection and transport in organic electronic devices but its solution processing has conventionally utilized undesirable di-n-alkyl sulfide solvents such as diethyl- (DES) and dipropyl-sulfide (DPS). Herein, this paper reports on the use of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) as alternative solvents for CuSCN interlayers and performs a detailed comparison of the resulting properties relative to films processed from DES and DPS and two other recent alternatives, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and ammonium hydroxide.
MIS-CELIV experiments were performed using the Fluxim PAIOS measurement platform with Characterization Suite 4.2 software.