Bulky cation diffusion in lead halide perovskite solar cells
Perini, Carlo and Rojas-Gatjens, Esteban and Ravello, Magdalena and Castro Mendez, Andres Felipe and Hidalgo, Juanita and An, Yu and Li, Ruipeng and Silva-Acuña, Carlos and Correa-Baena, Juan-Pablo
10 Sep 2021
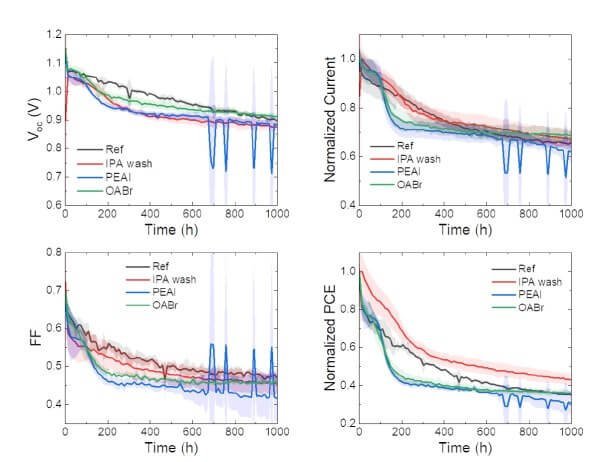
The impact on device stability of the bulky cation-modified interfaces in halide perovskite solar cells is not well-understood. In this paper the research team demonstrate the thermal instability of the bulky cation interface layers used in some of the highest performing solar cells to date.
The photovoltaic performance was evaluated using a Fluxim Litos Lite setup, equipped with a Wavelabs Sinus-70 AAA solar simulator with AM1.5 spectrum for excitation. The current voltage (J-V) characteristics were acquired with forward and reverse scans at a scan rate of 50 mV s-1. The stabilized power output was acquired using a maximum power point tracking algorithm for 60 s. Devices were not preconditioned before measurement. Masking was used during the measurement, defining a pixel area of 0.0625 cm2. Nitrogen was flown in the measurement chamber during characterization. No temperature control was applied. Aging tests were performed using a Fluxim Litos setup, using 1 Sun equivalent illumination with no UV-component, holding the substrates at 55 °C in a N2 atmosphere and using a maximum power point tracking algorithm. Every 12 h a J-V scan in reverse and forward direction was automatically acquired.