
Research Blogs
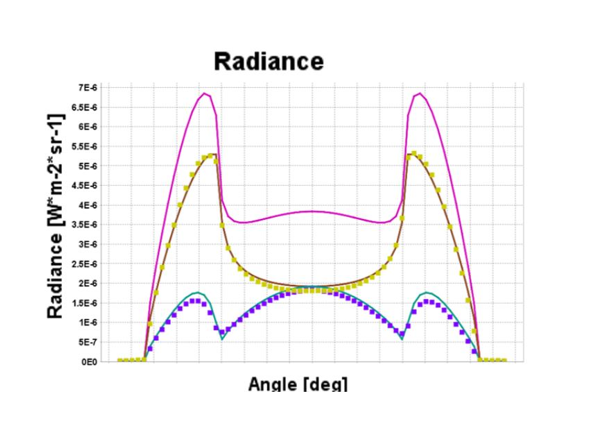
Angular Resolved Photoluminescence and Electroluminescence of light emitting materials
Setfos can analyze angular-dependent PL data collected by Phelos to get information about the properties of an organic emitter, such as the orientation of the dipoles and the width of the emission zone. With this analysis, we are able to optimize the characteristics of our OLEDs for high EQEs.

How to quantify Non-radiative voltage losses and recombination in solar cells
The open-circuit voltage (Voc) is the electrical potential difference between the two terminals of a solar cell, when there is no external load applied, hence no electric current flows. Correspondingly, this means that, when a voltage equivalent to the Voc is applied to the terminals of the solar cell, the recombination current (Jrec, which typically follows a non-ideal diode equation) and the photocurrent (Jph, the current generated by illuminating the solar cell) are equal, hence the net current is zero (Jrec=Jph at V= Voc).
Solar cells often present also non-radiative recombination mechanisms, in addition to the radiative one, as a result of poor material quality and non-idealities. To increase the Voc and thus potentially the power conversion efficiency, it is necessary to minimize the ΔVoc,nrad. It is, therefore, necessary to quantify the total loss and determine its origin.
Electroluminescence (EL) and photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) allow to directly extract the ΔVoc,nrad for thin-film solar cells such as perovskite solar cells, kesterite, perovskite, organic, or quantum dot. solar cells.
After quantifying the losses, the combination of capacitance-voltage (CV), temperature-dependent voltage characteristics (JV-T), and capacitance-frequency (Cf-T) measurements are essential to identify the recombination mechanisms.

EQE optimization For a Top-Emitting OLED
The external quantum efficiency (EQE) is the number of photons emitted by an OLED per number of injected charges. Photons are generated in the device emitting layer (EML), but most of the light is not escaping the device because of thee main loss mechanisms: Total Internal Reflection, Absorption Losses and Surface Plasmon Polaritons (SPPs). In this example, we are showing how to use Setfos to optimize the geometry of an OLED towards high light-outcoupling efficiency.
