Interfacial Engineering of a PCBM/AZO Electron Transport Bilayer for Efficient and Stable Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
Ali, U., Javed, S., Qureshi, A. A., Akram, M. A.,
Chem Nano Mat 2023, 9, e202300175.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202300175
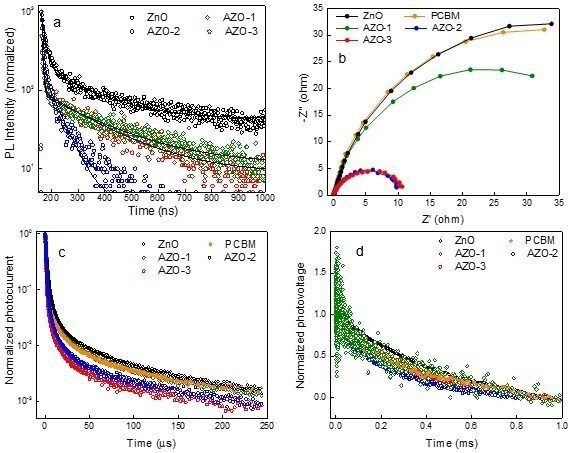
This research discusses the use of an interlayer of aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) nanoparticles to suppress interfacial recombination and improve the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells. The PCBM/AZO electron transport bilayer with an optimal concentration of 2% Al dopant exhibited greatly improved power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 18.63%, VOC of 1.13 V, and FF of 73% with negligible hysteresis index of 0.04.
How Paios was used
The TPC, TPV, and impedance measurements were performed using PAIOS from Fluxim. A pulse intensity for an optimized period was used to induce a spike in photovoltage and photo-current subsequently. The impedance spectra were taken from PAIOS v. 4.4 software, and scans were taken from 10 Hz to 2 MHz at a 0 V bias in the dark.